Cerebellar heterotopia of infancy in sudden infant death syndrome: an observational neuropathological study of four cases
- PMID: 32435901
- PMCID: PMC7577907
- DOI: 10.1007/s00414-020-02316-x
Cerebellar heterotopia of infancy in sudden infant death syndrome: an observational neuropathological study of four cases
Abstract
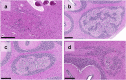
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is the sudden unexpected death of an infant < 1 year of age that remains unexplained after comprehensive workup including complete autopsy and investigation of the circumstances of death. The triple risk hypothesis posits that SIDS results as a combination of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the background of a predisposing vulnerability. Neuropathological examination in the past has focussed mainly on the brainstem as the major player in respiratory control, where subtle findings have been linked to the chain of events leading to death in SIDS. The cerebellum has received less attention, probably due to an assumed negligible role in central cardiorespiratory control. We report four cases of SIDS in which neuropathological investigation revealed cerebellar heterotopia of infancy, a distinct malformation of the cerebellum, and discuss the potential impact of this condition on the aetiology and pathogenesis of SIDS.
Keywords: Arousal circuits; Forensic neuropathology; Malformations of the central nervous system; SIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Krous HF, Beckwith JB, Byard RW, Rognum TO, Bajanowski T, Corey T, et al. Sudden infant death syndrome and unclassified sudden infant deaths: a definitional and diagnostic approach. Pediatrics. 2004;114:234–238. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell EA, Krous HF. Sudden unexpected death in infancy: a historical perspective. J Paediatr Child Health. 2015;51:108–112. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein RD, Blair PS, Sens MA, Shapiro-Mendoza CK, Krous HF, Rognum TO et al. Inconsistent classification of unexplained sudden deaths in infants and children hinders surveillance, prevention and research: recommendations from The 3rd International Congress on Sudden Infant and Child Death. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019;15:622–628. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Filiano JJ, Kinney HC. A perspective on neuropathologic findings in victims of the sudden infant death syndrome - the triple risk model. Biol Neonate. 1994;65:194–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

