EndoPredict® in early hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 32436145
- PMCID: PMC7275019
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-020-05688-1
EndoPredict® in early hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Evaluating consecutive early breast cancer patients, we analyzed both the impact of EndoPredict® on clinical decisions as well as clinico-pathological factors influencing the decision to perform this gene expression test.
Methods: Hormone receptor (HR)-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative early breast cancer patients treated between 2011 and 2016 were included in this study to investigate the role of EndoPredict® (EPclin) in the treatment of early breast cancer. A main study aim was to analyze the changes in therapy recommendations with and without EPclin. In addition, the impact of clinico-pathological parameters for the decision to perform EPclin was examined by Pearson's chi-squared test (χ2-test) and Fisher's exact test as well as univariate and multivariate logistic regressions.
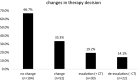
Results: In a cohort of 869 consecutive early HR-positive, HER-negative breast cancer patients, EPclin was utilized in 156 (18.0%) patients. EPclin led to changes in therapy recommendations in 33.3% (n = 52), with both therapy escalation in 19.2% (n = 30) and de-escalation in 14.1% (n = 22). The clinico-pathological factors influencing the use of EPclin were age (P < 0.001, odds ratio [OR] 0.498), tumor size (P = 0.011, OR 0.071), nodal status (P = 0.021, OR 1.674), histological grade (P = 0.043, OR 0.432), and Ki-67 (P < 0.001, OR 3.599).
Conclusions: EPclin led to a change in therapy recommendations in one third of the patients. Clinico-pathological parameters such as younger age, smaller tumor size, positive nodal status, intermediate histological grade and intermediate Ki-67 had a significant influence on the use of EndoPredict®.
Keywords: Early breast cancer; EndoPredict®; Endocrine therapy; Gene expression; Prognosis; Treatment decision.
Conflict of interest statement
K. Almstedt received speaker honoraria from Roche Pharma AG, Pfizer Pharma GmbH and AstraZeneca. M. Schmidt received honoraria for speaker or consultancy role from AMGEN, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, and Roche. He received research funding from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, Genentech, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, and Roche. He received travel reimbursement from Pfizer and Roche. M. Otto received honoraria for speaker or consultancy role from AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Roche and Sividon. He received travel reimbursement from AstraZeneca, and Boehringer-Ingelheim. MJ. Battista received honoraria for speaker or consultancy role from AstraZenca, MSD, PharmaMar, Roche Pharma AG, TEVA, Tesaro. He received travel reimbursement from Celgene, PharmaMar and Pierre Fabre. S. Krajnak received speaker honoraria from Roche. He received research funding from Novartis. He received travel reimbursement from PharmaMar. A. Hasenburg received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Celegen, MedConcept Gm, Med update GmbH, Medicultus, Pfizer, Promedicis GmbH, Pierre Fabre, Softconsult, Roche Pharma AG, Streamedup!GmbH and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. She is a member of the advisory board of PharmaMar, Promedicis GmbH, Pierre Fabre Pharma GmbH, Roche Pharma AG and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. She received research funding from Celgene. C. Denkert has been cofounder and shareholder of Sividon Diagnostics (now Myriad), has received speaker honoraria from Teva, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Amgen and has been consultant for MSD Oncology, Amgen, Roche and Daiichi-Sankyo. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peto R, Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Pan HC, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Taylor C, Wang YC, Bergh J, Di Leo A, Albain K, Swain S, Piccart M, Pritchard K. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):432–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61625-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris LN, Ismaila N, McShane LM, Andre F, Collyar DE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hammond EH, Kuderer NM, Liu MC, Mennel RG, Van Poznak C, Bast RC, Hayes DF. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(10):1134–1150. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.65.2289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Curigliano G, Burstein HJ, Winer EP, Gnant M, Dubsky P, Loibl S, Colleoni M, Regan MM, Piccart-Gebhart M, Senn HJ, Thurlimann B, Andre F, Baselga J, Bergh J, Bonnefoi H, Brucker SY, Cardoso F, Carey L, Ciruelos E, Cuzick J, Denkert C, Di-Leo A, Ejlertsen B, Francis P, Galimberti V, Garber J, Gulluoglu B, Goodwin P, Harbeck N, Hayes DF, Huang CS, Huober J, Hussein K, Jassem J, Jiang Z, Karlsson P, Morrow M, Orecchia R, Osborne KC, Pagani O, Partridge AH, Pritchard K, Ro J, Rutgers EJT, Sedlmayer F, Semiglazov V, Shao Z, Smith I, Toi M, Tutt A, Viale G, Watanabe T, Whelan TJ, Xu B (2017) De-escalating and escalating treatments for early-stage breast cancer: the St Gallen International Expert Consensus Conference on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2017. Annals of Oncology 28 (8):1700–1712 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krop I, Ismaila N, Andre F, Bast RC, Barlow W, Collyar DE, Hammond ME, Kuderer NM, Liu MC, Mennel RG, Van Poznak C, Wolff AC, Stearns V. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(24):2838–2847. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.74.0472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous