Asymmetrical cortical vessel sign predicts prognosis after acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 32436291
- PMCID: PMC7375089
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1657
Asymmetrical cortical vessel sign predicts prognosis after acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
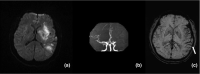
Introduction: To assess whether the asymmetrical cortical vessel sign (ACVS) on susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) could predict 90-day poor outcomes in anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-tPA).
Methods: Clinical data of consecutive patients with anterior circulation AIS treated with r-tPA were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical variables included age, sex, vascular risk factors, NIHSS score, onset to treatment time, and initial hematologic and neuroimaging findings. Follow-up was performed 90 days after onset. Poor outcome was defined as a modified Rankin scale (mRS) ≥3 at 90 days.
Results: A total of 145 patients were included, 35 (24.1%) patients presented with ACVS (≥Grade 1) on SWI. Fifty-three (36.6%) patients had a poor outcome at 90 days. ACVS (≥Grade 1) occurred in 21 (39.6%) patients with poor outcome compared with 14 (15.2%) patients with favorable outcome (p = .001). Univariate analysis indicated that age, NIHSS score on admission, previous stroke, hemorrhagic transformation, severe intracranial large artery stenosis or occlusion (SILASO), and ACVS were associated with 90-day poor outcome (p < .05). Since SILASO and ACVS were highly correlated and ACVS had different grades, we used three logistic regression models. Results from the three models showed that ACVS was associated with 90-day poor outcome.
Conclusions: In r-tPA-treated patients with anterior circulation AIS, ACVS might be a helpful neuroimaging predictor for poor outcome at 90 days.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; asymmetrical cortical vessel sign; intravenous thrombolysis; outcome; susceptibility-weighted imaging.
© 2020 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Adams Jr, H. P. , Bendixen, B. H. , Kappelle, L. J. , Biller, J. , Love, B. B. , Gordon, D. L. , & Marsh 3rd, E. E. (1993). Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke, 24, 35–41. 10.1161/01.str.24.1.35 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adams, H. P. , Davis, P. H. , Leira, E. C. , Chang, K. C. , Bendixen, B. H. , Clarke, W. R. , … Hansen, M. D. (1999). Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: A report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology, 53, 126–131. 10.1212/wnl.53.1.126 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

