Myelin-Associated MAL and PLP Are Unusual among Multipass Transmembrane Proteins in Preferring Ordered Membrane Domains
- PMID: 32436385
- PMCID: PMC7792449
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c03028
Myelin-Associated MAL and PLP Are Unusual among Multipass Transmembrane Proteins in Preferring Ordered Membrane Domains
Abstract
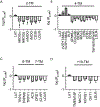
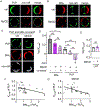
Eukaryotic membranes can be partitioned into lipid-driven membrane microdomains called lipid rafts, which function to sort lipids and proteins in the plane of the membrane. As protein selectivity underlies all functions of lipid rafts, there has been significant interest in understanding the structural and molecular determinants of raft affinity. Such determinants have been described for lipids and single-spanning transmembrane proteins; however, how multipass transmembrane proteins (TMPs) partition between ordered and disordered phases has not been widely explored. Here we used cell-derived giant plasma membrane vesicles (GPMVs) to systematically measure multipass TMP partitioning to ordered membrane domains. Across a set of 24 structurally and functionally diverse multipass TMPs, the large majority (92%) had minimal raft affinity. The only exceptions were two myelin-associated four-pass TMPs, myelin and lymphocyte protein (MAL), and proteo lipid protein (PLP). We characterized the potential mechanisms for their exceptional raft affinity and observed that PLP requires cholesterol and sphingolipids for optimal association with ordered membrane domains and that PLP and MAL appear to compete for cholesterol-mediated raft affinity. These observations suggest broad conclusions about the composition of ordered membrane domains in cells and point to previously unrecognized drivers of raft affinity for multipass transmembrane proteins.
Figures
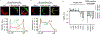



Similar articles
-
Perfringolysin O association with ordered lipid domains: implications for transmembrane protein raft affinity.Biophys J. 2010 Nov 17;99(10):3255-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.028. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 21081073 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of protein partitioning into ordered membrane domains and lipid rafts.Chem Phys Lipids. 2015 Nov;192:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Chem Phys Lipids. 2015. PMID: 26241883 Review.
-
Ceramide selectively displaces cholesterol from ordered lipid domains (rafts): implications for lipid raft structure and function.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 12;279(11):9997-10004. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309992200. Epub 2003 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14699154
-
Partitioning to ordered membrane domains regulates the kinetics of secretory traffic.Elife. 2024 Jun 5;12:RP89306. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89306. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38837189 Free PMC article.
-
Raft membrane domains: from a liquid-ordered membrane phase to a site of pathogen attack.Semin Immunol. 2001 Apr;13(2):89-97. doi: 10.1006/smim.2000.0300. Semin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11308292 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 requires cholesterol for viral entry and pathological syncytia formation.Elife. 2021 Apr 23;10:e65962. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65962. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33890572 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Phenomena in Plasma Membrane Organization and Function.Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2021 Apr 20;72:51-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-090419-115951. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2021. PMID: 33710910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central role of Prominin-1 in lipid rafts during liver regeneration.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 20;13(1):6219. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33969-4. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36266314 Free PMC article.
-
MALL, a membrane-tetra-spanning proteolipid overexpressed in cancer, is present in membraneless nuclear biomolecular condensates.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Apr 10;79(5):236. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04270-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35399121 Free PMC article.
-
Human myelin proteolipid protein structure and lipid bilayer stacking.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 12;79(8):419. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04428-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35829923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lingwood D; Simons K, Detergent resistance as a tool in membrane research. Nature Protocols 2007, 2 (9), 2159–2165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

