Visualization of putative coronavirus in kidney
- PMID: 32437764
- PMCID: PMC7206426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.004
Visualization of putative coronavirus in kidney
Figures
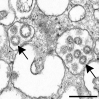
Comment in
-
The authors reply.Kidney Int. 2020 Jul;98(1):232-233. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.007. Epub 2020 May 16. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32425266 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The authors reply.Kidney Int. 2020 Jul;98(1):232. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.002. Epub 2020 May 8. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32437769 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China.Kidney Int. 2020 Jul;98(1):219-227. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32327202 Free PMC article.
-
Collapsing glomerulopathy in a COVID-19 patient.Kidney Int. 2020 Jul;98(1):228-231. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32471639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Miller S.E. Diagnosis of viral infection by electron microscopy. In: Lennette E.H., Lennette D.A., Lennette E.T., editors. Diagnostic Procedures for Viral, Rickettsial and Chlamydial Infections. American Public Health Association; Washington, DC: 1995. pp. 35–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

