SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32437830
- PMCID: PMC7211738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.002
SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Background & aims: Liver enzyme abnormalities are common in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Whether or not severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection can lead to liver damage per se remains unknown. Herein, we reported the clinical characteristics and liver pathological manifestations of COVID-19 patients with liver enzyme abnormalities.
Methods: We analyzed 156 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from 2 designated centers in China and compared clinical features between patients with or without elevated aminotransferases. Postmortem liver biopsies were obtained from 2 cases who had elevated aminotransferases. We investigated the patterns of liver impairment by electron microscopy, immunohistochemistry, TUNEL assay and pathological studies.
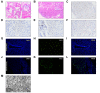
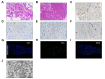
Results: Sixty-four out of 156 (41.0%) patients with COVID-19 had elevated aminotransferases. The median levels of alanine aminotransferase were 50 U/L vs. 19 U/L, respectively, aspartate aminotransferase were 45.5 U/L vs. 24 U/L, respectively in abnormal and normal aminotransferase groups. Liver enzyme abnormalities were associated with disease severity, as well as a series of laboratory tests including higher alveolar-arterial oxygen partial pressure difference, higher gamma-glutamyltransferase, lower albumin, decreased CD4+ T cells and B lymphocytes. Ultrastructural examination identified typical coronavirus particles, characterized by spike structures, in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes in 2 COVID-19 cases. SARS-CoV-2-infected hepatocytes displayed conspicuous mitochondrial swelling, endoplasmic reticulum dilatation and glycogen granule decrease. Histologically, massive hepatic apoptosis and some binuclear hepatocytes were observed. Taken together, both ultrastructural and histological evidence indicated a typical lesion of viral infection. Immunohistochemical results showed scarce CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. No obvious eosinophil infiltration, cholestasis, fibrin deposition, granuloma, massive central necrosis, or interface hepatitis were observed.
Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2 infection in the liver directly contributes to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19. Hence, a surveillance of viral clearance in liver and long-term outcome of COVID-19 is required.
Lay summary: Liver enzyme abnormalities are common in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We reported the clinical characteristics and liver pathological manifestations of COVID-19 patients with elevated liver enzymes. Our findings suggested that SARS-CoV-2 infection of the liver is a crucial factor contributing to hepatic impairment in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytopathy; Liver enzyme abnormality; SARS-CoV-2 infection; Transaminase.
© 2020 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures

Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 related liver impairment - perception may not be the reality.J Hepatol. 2020 Oct;73(4):991-992. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.025. Epub 2020 May 23. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32454042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Single cell RNA sequencing analysis did not predict hepatocyte infection by SARS-CoV-2.J Hepatol. 2020 Oct;73(4):993-995. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.030. Epub 2020 May 28. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32473193 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SARS-CoV-2: Is the liver merely a bystander to severe disease?J Hepatol. 2020 Oct;73(4):995-996. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.035. Epub 2020 Jun 2. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32502510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Liver damage at admission is an independent prognostic factor for COVID-19.J Dig Dis. 2020 Sep;21(9):512-518. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12925. J Dig Dis. 2020. PMID: 32713118
-
Clinical characteristics of non-ICU hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and liver injury: A retrospective study.Liver Int. 2020 Jun;40(6):1321-1326. doi: 10.1111/liv.14449. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Liver Int. 2020. PMID: 32239591 Free PMC article.
-
Severe COVID-19 patients with liver injury: a seven-case series.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jul;24(14):7855-7860. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202007_22290. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32744713
-
Kinetic patterns of liver enzyme elevation with COVID-19 in the USA.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;32(11):1466-1469. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001792. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32501877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the liver: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Hepatol Int. 2020 Sep;14(5):711-722. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10071-9. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Hepatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32623633 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mild versus Severe Liver Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Dig Dis. 2021;39(1):52-57. doi: 10.1159/000510758. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 32777784 Free PMC article.
-
Liver histopathology in COVID-19 patients: A mono-Institutional series of liver biopsies and autopsy specimens.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 May;221:153451. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153451. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33932720 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to the Asialoglycoprotein Receptor on Human Primary Hepatocytes and Immortalized Hepatocyte-Like Cells by Confocal Analysis.Hepat Med. 2021 Apr 14;13:37-44. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S301979. eCollection 2021. Hepat Med. 2021. PMID: 33883951 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning insights concerning inflammatory and liver-related risk comorbidities in non-communicable and viral diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 28;28(44):6230-6248. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i44.6230. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36504554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on Covid-19: vaccines, timing of transplant after COVID-19 infection and use of positive donors.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2023 Apr 1;28(2):76-84. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000001056. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2023. PMID: 36809306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

