Causes of fever in primary care in Southeast Asia and the performance of C-reactive protein in discriminating bacterial from viral pathogens
- PMID: 32437937
- PMCID: PMC7211754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.016
Causes of fever in primary care in Southeast Asia and the performance of C-reactive protein in discriminating bacterial from viral pathogens
Abstract
Objectives: This study investigated causes of fever in the primary levels of care in Southeast Asia, and evaluated whether C-reactive protein (CRP) could distinguish bacterial from viral pathogens.
Methods: Blood and nasopharyngeal swab specimens were taken from children and adults with fever (>37.5 °C) or history of fever (<14 days) in Thailand and Myanmar.
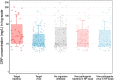
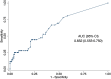
Results: Of 773 patients with at least one blood or nasopharyngeal swab specimen collected, 227 (29.4%) had a target organism detected. Influenza virus type A was detected in 85/227 cases (37.5%), followed by dengue virus (30 cases, 13.2%), respiratory syncytial virus (24 cases, 10.6%) and Leptospira spp. (nine cases, 4.0%). Clinical outcomes were similar between patients with a bacterial or a viral organism, regardless of antibiotic prescription. CRP was higher among patients with a bacterial organism compared with those with a viral organism (median 18 mg/L, interquartile range [10-49] versus 10 mg/L [≤8-22], p = 0.003), with an area under the curve of 0.65 (95% CI 0.55-0.75).
Conclusions: Serious bacterial infections requiring antibiotics are an exception rather than the rule in the first line of care. CRP testing could assist in ruling out such cases in settings where diagnostic uncertainty is high and routine antibiotic prescription is common. The original CRP randomised controlled trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02758821.
Keywords: Antibiotic prescription; C-reactive protein; Causes of fever; Primary care; Southeast Asia.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in study design, data collection, data interpretation or writing the manuscript. The corresponding author had full access to all the data and took the final decision to submit for publication.
Figures
References
-
- Althaus T., Greer R.C., Swe M.M.M., Cohen J., Tun N.N., Heaton J. Effect of point-of-care C-reactive protein testing on antibiotic prescription in febrile patients attending primary care in Thailand and Myanmar: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(1):e119–e131. doi: 10.1016/s2214-109x(18)30444-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell G. Advances in statistical methodology for the evaluation of diagnostic and laboratory tests. Stat Med. 1994;13(5–7):499–508. Epub 1994/03/15. PubMed PMID: 8023031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

