Diabetes and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for COVID-19
- PMID: 32438331
- PMCID: PMC7205616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.013
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for COVID-19
Abstract
Background and aims: Clinical evidence exists that patients with diabetes are at higher risk for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We investigated the physiological origins of this clinical observation linking diabetes with severity and adverse outcome of COVID-19.
Methods: Publication mining was applied to reveal common physiological contexts in which diabetes and COVID-19 have been investigated simultaneously. Overall, we have acquired 1,121,078 publications from PubMed in the time span between 01-01-2000 and 17-04-2020, and extracted knowledge graphs interconnecting the topics related to diabetes and COVID-19.
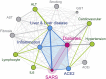
Results: The Data Mining revealed three pathophysiological pathways linking diabetes and COVID-19. The first pathway indicates a higher risk for COVID-19 because of a dysregulation of Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. The other two important physiological links between diabetes and COVID-19 are liver dysfunction and chronic systemic inflammation. A deep network analysis has suggested clinical biomarkers predicting the higher risk: Hypertension, elevated serum Alanine aminotransferase, high Interleukin-6, and low Lymphocytes count.
Conclusions: The revealed biomarkers can be applied directly in clinical practice. For newly infected patients, the medical history needs to be checked for evidence of a long-term, chronic dysregulation of these biomarkers. In particular, patients with diabetes, but also those with prediabetic state, deserve special attention.
Keywords: ACE2; Hypertension; Inflammation; Liver dysfunction; SARS-Coronavirus-2.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
"Does having diabetes increase chances of contracting COVID-19 infection?".Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Sep-Oct;14(5):765-766. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.048. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32512520 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. J Am Med Assoc. 2020;323:1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

