ddPCR: a more accurate tool for SARS-CoV-2 detection in low viral load specimens
- PMID: 32438868
- PMCID: PMC7448897
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1772678
ddPCR: a more accurate tool for SARS-CoV-2 detection in low viral load specimens
Abstract
Quantitative real time PCR (RT-PCR) is widely used as the gold standard for clinical detection of SARS-CoV-2. However, due to the low viral load specimens and the limitations of RT-PCR, significant numbers of false negative reports are inevitable, which results in failure to timely diagnose, cut off transmission, and assess discharge criteria. To improve this situation, an optimized droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) was used for detection of SARS-CoV-2, which showed that the limit of detection of ddPCR is significantly lower than that of RT-PCR. We further explored the feasibility of ddPCR to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA from 77 patients, and compared with RT-PCR in terms of the diagnostic accuracy based on the results of follow-up survey. 26 patients of COVID-19 with negative RT-PCR reports were reported as positive by ddPCR. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, negative likelihood ratio (NLR) and accuracy were improved from 40% (95% CI: 27-55%), 100% (95% CI: 54-100%), 100%, 16% (95% CI: 13-19%), 0.6 (95% CI: 0.48-0.75) and 47% (95% CI: 33-60%) for RT-PCR to 94% (95% CI: 83-99%), 100% (95% CI: 48-100%), 100%, 63% (95% CI: 36-83%), 0.06 (95% CI: 0.02-0.18), and 95% (95% CI: 84-99%) for ddPCR, respectively. Moreover, 6/14 (42.9%) convalescents were detected as positive by ddPCR at 5-12 days post discharge. Overall, ddPCR shows superiority for clinical diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 to reduce the false negative reports, which could be a powerful complement to the RT-PCR.
Keywords: RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2; clinical detection; droplet digital PCR; false negative.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
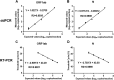
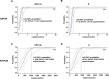

References
-
- World Health Organization . Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Feb 4]. p. 1–7. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/laboratory-testing-for-2019-nove....
-
- General Office of the National Health and Health Commission O of the SA of TCM . Diagnosis and treatment of pneumonitis with a new type of coronavirus infection (trial version 5) [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Feb 6]. Available from: http://bgs.satcm.gov.cn/zhengcewenjian/2020-02-06/12848.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
