Detection and quantification of glycosylated queuosine modified tRNAs by acid denaturing and APB gels
- PMID: 32439717
- PMCID: PMC7430669
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.075556.120
Detection and quantification of glycosylated queuosine modified tRNAs by acid denaturing and APB gels
Abstract
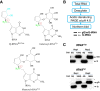
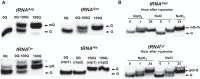
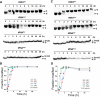
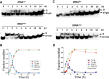
Queuosine (Q) is a conserved tRNA modification in bacteria and eukaryotes. Eukaryotic Q-tRNA modification occurs through replacing the guanine base with the scavenged metabolite queuine at the wobble position of tRNAs with
Keywords: acid denaturing PAGE; galactosyl-queuosine; mannosyl-queuosine; queuosine.
© 2020 Zhang et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative probing of glycosylated queuosine modifications in tRNA.Methods Enzymol. 2021;658:73-82. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2021.06.003. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Methods Enzymol. 2021. PMID: 34517960
-
Glycosylated queuosines in tRNAs optimize translational rate and post-embryonic growth.Cell. 2023 Dec 7;186(25):5517-5535.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.10.026. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37992713
-
Synthesis of Galactosyl-Queuosine and Distribution of Hypermodified Q-Nucleosides in Mouse Tissues.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Jul 20;59(30):12352-12356. doi: 10.1002/anie.202002295. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32160400 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis and roles of tRNA queuosine modification and its glycosylated derivatives in human health and diseases.Cell Chem Biol. 2025 Feb 20;32(2):227-238. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.11.004. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Cell Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39657672 Review.
-
Queuosine modification of tRNA: its divergent role in cellular machinery.Biosci Rep. 2009 Nov 23;30(2):135-48. doi: 10.1042/BSR20090057. Biosci Rep. 2009. PMID: 19925456 Review.
Cited by
-
A dual-purpose polymerase engineered for direct sequencing of pseudouridine and queuosine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 8;51(8):3971-3987. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad177. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36971106 Free PMC article.
-
O-glycosylation contributes to mammalian glycoRNA biogenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2024.08.28.610074. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.28.610074. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39257776 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Queuosine is incorporated into precursor tRNA before splicing.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 31;16(1):7044. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62220-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40745156 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of queuosine and 2-thio tRNA modifications by high throughput sequencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Sep 23;50(17):e99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac517. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35713550 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and function of 7-deazaguanine derivatives in bacteria and phages.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Mar 27;88(1):e0019923. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00199-23. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38421302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Costa A, de Barros JP P, Keith G, Baranowski W, Desgres J. 2004. Determination of queuosine derivatives by reverse-phase liquid chromatography for the hypomodification study of Q-bearing tRNAs from various mammal liver cells. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 801: 237–247. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.11.022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
