Gravitational-wave asteroseismology with fundamental modes from compact binary inspirals
- PMID: 32439905
- PMCID: PMC7242351
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15984-5
Gravitational-wave asteroseismology with fundamental modes from compact binary inspirals
Abstract
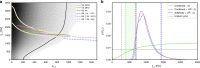
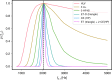
Gravitational waves (GWs) from binary neutron stars encode unique information about ultra-dense matter through characterisic signatures associated with a variety of phenomena including tidal effects during the inspiral. The main tidal signature depends predominantly on the equation of state (EoS)-related tidal deformability parameter Λ, but at late times is also characterised by the frequency of the star's fundamental oscillation mode (f-mode). In General Relativity and for nuclear matter, Λ and the f-modes are related by universal relations which may not hold for alternative theories of gravity or exotic matter. Independently measuring Λ and the f-mode frequency enables tests of gravity and the nature of compact binaries. Here we present directly measured constraints on the f-mode frequencies of the companions of GW170817. We also show that future GW detector networks will measure f-mode frequencies to within tens of Hz, enabling precision GW asteroseismology with binary inspiral signals alone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott BP, et al. GW170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017;119:161101. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan EE, Hinderer T. Constraining neutron star tidal Love numbers with gravitational wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D. 2008;77:021502.
-
- Hinderer T, et al. Effects of neutron-star dynamic tides on gravitational waveforms within the effective-one-body approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016;116:181101. - PubMed
-
- Steinhoff J, Hinderer T, Buonanno A, Taracchini A. Dynamical tides in general relativity: effective action and effective-one-body Hamiltonian. Phys. Rev. D. 2016;94:104028.
-
- Schmidt P, Hinderer T. Frequency domain model of f -mode dynamic tides in gravitational waveforms from compact binary inspirals. Phys. Rev. D. 2019;100:021501.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

