MED15, transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), FcγRIII (CD16), and HNK-1 (CD57) are prognostic biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32439976
- PMCID: PMC7242386
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65145-3
MED15, transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), FcγRIII (CD16), and HNK-1 (CD57) are prognostic biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
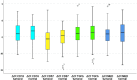
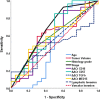
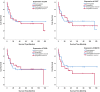
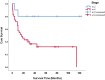
Owing to the high incidence and mortality of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), knowledge of its diagnostic and prognostic factors is of significant value. The biomarkers 'CD16, CD57, transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), and MED15' can play crucial roles in tumorigenesis, and hence might contribute to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Since there was no previous study on MED15 in almost all cancers, and since the studies on diagnostic/prognostic values of the other three biomarkers were a few in OSCC (if any) and highly controversial, this study was conducted. Biomarker expressions in all OSCC tissues and their adjacent normal tissues available at the National Tumor Bank (n = 4 biomarkers × [48 cancers + 48 controls]) were estimated thrice using qRT-PCR. Diagnostic values of tumors were assessed using receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curves. Factors contributing to patients' survival over 10 years were assessed using multiple Cox regressions. ROC curves were used to estimate cut-off points for significant prognostic variables (α = 0.05). Areas under the curve pertaining to diagnostic values of all markers were non-significant (P > 0.15). Survival was associated positively with tumoral upregulation of TGF-β1 and downregulation of CD16, CD57, and MED15. It was also associated positively with younger ages, lower histological grades, milder Jacobson clinical TNM stages (and lower pathological Ns), smaller and thinner tumors, and surgery cases not treated with incisional biopsy (Cox regression, P < 0.05). The cut-off point for clinical stage -as the only variable with a significant area under the curve- was between the stages 2 and 3. Increased TGF-β1 and reduced CD16, CD57, and MED15 expressions in the tumor might independently favor the prognosis. Clinical TNM staging might be one of the most reliable prognostic factors, and stages above 2 can predict a considerably poorer prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- O-Charoenrat P, Rhys-Evans PH, Eccles SA. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors correlates with invasion and metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:813–820. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

