GSEA-assisted gene signatures valid for combinations of prognostic markers in PCNSL
- PMID: 32439996
- PMCID: PMC7242340
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65463-6
GSEA-assisted gene signatures valid for combinations of prognostic markers in PCNSL
Abstract
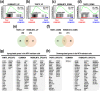
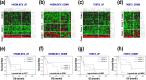
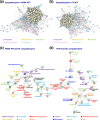
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a brain malignant non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma. The standard treatments are high-dose methotrexate (MTX)-based chemotherapies and deferred whole brain radiotherapy. However, MTX resistance-dependent global expression and signaling pathway changes and their relationship with prognoses have not yet been elucidated. Here, we conducted a global expression analysis with next-generation sequencing and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) in MTX-resistant PCNSL cell lines (HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX) and PCNSL tissues. In rank scores, genes listed in HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX were enriched in PCNSL with poor prognoses. In fold changes, a part of differentially-expressed genes in PCNSL tissues were also detected in HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX cells; FOXD2-AS1 and MMP19 were commonly expressed in both HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX, FABP5 and CD70 were HKBML-MTX-specifically expressed, and CLCN2, HOXB9, INE1, and LRP5L were TK-MTX-specifically expressed, which may provide a combination of prognostic markers on MTX-sensitivities in PCNSL. Additionally, PCNSL subgroups, divided with hierarchical clustering and Kaplan-Meier methods, included twenty commonly expressed genes in both HKBML-MTX and TK-MTX, ten HKBML-MTX-specifically expressed genes, and two TK-MTX-specifically expressed genes. These results suggest that the GSEA-assisted gene signatures can provide a combination for prognostic markers in recurrent PCNSL with MTX resistances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ricard D, et al. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 2012;379:1984–1996. - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. - PubMed
-
- Goecke IA, et al. Methotrexate regulates the expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta isoforms in normal human peripheral mononuclear cells and human lymphocyte cell lines in vitro. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:2115–2123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

