Dupilumab: Clinical Efficacy of Blocking IL-4/IL-13 Signalling in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
- PMID: 32440101
- PMCID: PMC7217316
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S243053
Dupilumab: Clinical Efficacy of Blocking IL-4/IL-13 Signalling in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
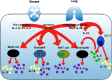
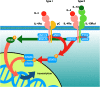
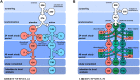
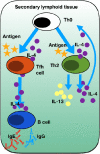
In September 2019, The Lancet published details of two large Phase III double-blind placebo-controlled studies (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52) confirming the clinical efficacy of the biologic dupilumab in simultaneously blocking both IL-4/IL-13 signalling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP). The studies demonstrated that dupilumab (Dupixent®, Sanofi and Regeneron) 300mg subcutaneously administered was clinically effective when added for patients with moderate to severe CRSwNP already maintained on the standard intranasal steroid mometasone furoate. Duration of treatment ranged from injections either 2 weekly for 24 weeks (SINUS-24) or every 2 weeks for 52 weeks or finally every 2 weeks for 24 weeks stepping down thereafter to every 4 weeks for a further 28 weeks (SINUS-52). Rapid improvements in all important parameters of disease burden were seen with such improvement maintained even where the frequency of injections was decreased. In patients with co-existent asthma, lung function and asthma control scores improved. This is consistent with the one airway hypothesis of shared T2 inflammatory programmes driving both disease syndromes. The studies formed the basis for FDA registration and clinical launch in the US, and EMA approval in Europe. Dupilumab presents a significant new treatment option in an area of urgent unmet therapeutic need in CRSwNP. Should dupilumab prove to be as effective in the real-life clinical environment as it has been in the studies, then a paradigm shift from sinonasal surgery to medical treatment of CRSwNP may need to occur in the ENT community. Questions in relation to best patient selection, combined upper and lower airway therapeutic pathways, long-term safety along with health economics and cost constraints ought now to be addressed.
Keywords: biologic; inflammation; monoclonal antibody; sinusitis; therapeutics.
© 2020 Kariyawasam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HHK has undertaken paid consultancy work for Sanofi and Novartis and received lecture fees and support for conference attendance from GSK. HHK has undertaken paid lecture commitment work for AstraZeneca. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials.Lancet. 2019 Nov 2;394(10209):1638-1650. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31881-1. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31543428 Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: mechanistic insights from targeting IL-4 and IL-13 via IL-4Rα inhibition with dupilumab.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Dec;16(12):1115-1125. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1847083. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33148074 Review.
-
Dupilumab: A Review in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Drugs. 2020 May;80(7):711-717. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01298-9. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32240527 Review.
-
Dupilumab reduces local type 2 pro-inflammatory biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis.Allergy. 2019 Apr;74(4):743-752. doi: 10.1111/all.13685. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30488542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dupilumab improves upper and lower airway disease control in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021 May;126(5):584-592.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33465455 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Dupilumab in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Real-Life Data in Tertiary Care.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;16(4):630. doi: 10.3390/ph16040630. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111387 Free PMC article.
-
The Interleukin-15 and Interleukin-8 Axis as a Novel Mechanism for Recurrent Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 29;12(5):980. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12050980. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790942 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab (Dupixent®) tends to be an effective therapy for uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: real data of a single-centered, retrospective single-arm longitudinal study from a university hospital in Germany.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Apr;280(4):1741-1755. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07679-y. Epub 2022 Oct 15. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36242612 Free PMC article.
-
Computational fluid dynamic modeling of the effect of dupilumab in the management of anosmia secondary to chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022 Dec;12(12):1578-1580. doi: 10.1002/alr.23050. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022. PMID: 35765860 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Targeting IgE with Anti-IgE Omalizumab Therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Dec 10;14:5483-5494. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S226575. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33328726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020;58(Suppl S29):1–464. - PubMed
-
- Smith KA, Orlandi RR, Rudmik L. Cost of adult chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(7):1547–1556. - PubMed
-
- DeConde AS, Soler ZM. Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and burden of disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016;30(2):134–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

