Etiology of Respiratory Complications among Iranian HIV Infected Patients
- PMID: 32440296
- PMCID: PMC7230122
Etiology of Respiratory Complications among Iranian HIV Infected Patients
Abstract
Background: Infection with Human Immune deficiency Virus (HIV) is a growing problem in developing countries. Among HIV infected cases, respiratory complications are common, dissimilar in different setting and their diagnosis is challenging. The aim of this study was to determine the spectrum of infectious and non-infectious pulmonary complications among HIV infected patients.
Materials and methods: The retrospective study was done among 710 HIV infected patients admitted in Masih Daneshvari Hospital, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases, Tehran, Iran from January 2003 to March 2017. Demographic, clinical, radiologic and laboratory data of 836 episodes of pulmonary complications were reviewed and final diagnosis were extracted.
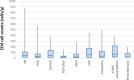
Results: Mean of CD4 cell count was 90±131 ×106 cells/L. Definite etiology was found for 653 episodes (78.1%) of pulmonary complications. Infectious respiratory diseases were clearly more common than non-infectious etiologies, 86.1 and 7.6%, respectively. Pulmonary tuberculosis, as the leading cause, involved 542 cases (64.8%) and Pneumocystis jiroveci (P. jiroveci) was the second infectious agent that was found in 111 cases (13.2%). Among non- infectious causes, bronchiectasis and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) exacerbation were on the top of the list, 21 of 64 (32.8%) and 18 0f 64 (28.1%), respectively. Many patients had more than one etiology. P. jiroveci had the highest tendency for dual infections (43 episodes).
Conclusion: Pulmonary complications, especially infections are common among HIV cases in Iran, among them tuberculosis is the most common. Respiratory problems may be the first presentation of HIV infection. Clinicians should be aware about the risk of dual infections. Screening for HIV among all tuberculosis cases and vice versa is recommend.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; Pulmonary; Respiratory complications; Tuberculosis.
Copyright© 2019 National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Respiratory Complications in Iranian Hospitalized Patients with HIV/AIDS.Tanaffos. 2011;10(3):49-54. Tanaffos. 2011. PMID: 25191376 Free PMC article.
-
Etiology of pulmonary complications of human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected patients in Taiwan in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: a prospective observational study.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013 Dec;46(6):433-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Sep 29. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23026388
-
Clinical features of tuberculosis associated with HIV infection in Taiwan.J Formos Med Assoc. 1996 Dec;95(12):923-8. J Formos Med Assoc. 1996. PMID: 9000809
-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related pulmonary complications in pregnancy.Semin Perinatol. 1997 Aug;21(4):336-50. doi: 10.1016/s0146-0005(97)80077-8. Semin Perinatol. 1997. PMID: 9298723 Review.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Global prevalence, mortality, and main characteristics of HIV-associated pneumocystosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 25;19(3):e0297619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297619. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38526997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization HIV/AIDS [cited 21 February 2018]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs360/en/.
-
- UNAIDS HIV and AIDS estimates (2016) [cited February 21, 2018]. Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/islamicrepublicofiran/.
-
- Benito N, Moreno A, Miro JM, Torres A. Pulmonary infections in HIV-infected patients: an update in the 21st century. Eur Respir J 2012;39(3):730–45. - PubMed
-
- Miller R. HIV-associated respiratory diseases. Lancet 1996;348(9023):307–12. - PubMed
-
- Feikin DR, Feldman C, Schuchat A, Janoff EN. Global strategies to prevent bacterial pneumonia in adults with HIV disease. Lancet Infect Dis 2004;4(7):445–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials