Genus Boswellia as a new candidate for neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 32440312
- PMCID: PMC7229515
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2020.35288.8419
Genus Boswellia as a new candidate for neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
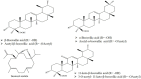
Neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by progressive loss of neurons, share common mechanisms such as apoptotic cell death, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Genus Boswellia is a genus in the Burseraceae family. It comprises several species traditionally used for treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases, cerebral edema, chronic pain syndrome, gastrointestinal diseases, tumors, as well as enhancing intelligence. Many studies have been carried out to discover therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's diseases, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, stroke, and concomitant cognitive deficits. However, no curative treatment has been developed. This paper provides an overview of evidence about the potential of the Boswellia species and their main constituents, boswellic acids, as modulators of several mechanisms involved in the pathology of the neurodegenerative diseases. In vitro, animal, and clinical studies have confirmed that Boswellia species contain bioactive components that may enhance cognitive activity and protect against neurodegeneration. They exert the beneficial effects via targeting multiple pathological causes by antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antiamyloidogenic, and anti-apoptotic properties. The Boswellia species, having neuroprotective potential, makes them a promising candidate to cure or prevent the neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s diseases; Boswellia; Cognitive; Neurodegenerative; diseases Neuroprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson's disease treatment.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Jun 17;19(1):20240988. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0988. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 38911256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 14;2020:6565396. doi: 10.1155/2020/6565396. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32148547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroprotective effects of targeting key factors of neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: The role of ER stress, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 6;17:1105247. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1105247. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36950516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and drug targets via apoptotic signaling.Mitochondrion. 2019 Nov;49:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Mitochondrion. 2019. PMID: 31288090 Review.
-
Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular stress response in Friedreich's ataxia.J Neurol Sci. 2005 Jun 15;233(1-2):145-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2005.03.012. J Neurol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15896810 Review.
Cited by
-
The Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Activities of Natural Products to Control Autoimmune Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):95. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010095. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Placebo-Controlled, Pseudo-Randomized, Crossover Trial of Botanical Agents for Gulf War Illness: Curcumin (Curcuma longa), Boswellia (Boswellia serrata), and French Maritime Pine Bark (Pinus pinaster).Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 3;18(5):2468. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052468. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33802272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence-Based Opinions from Multidisciplinary Experts on Use of Naturopathic Herbal Remedies in Pain Management.J Pain Res. 2024 Feb 8;17:599-608. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S432090. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38347854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Frankincense (Boswellia serrata) Oil Modulates the Growth, Intestinal Morphology, the Fatty Acid Composition of Breast Muscle, Immune Status, and Immunoexpression of CD3 and CD20 in Broiler Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;13(6):971. doi: 10.3390/ani13060971. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978513 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Role of Nutraceuticals in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1328:243-253. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34981482 Review.
References
-
- Winner B, Kohl Z, Gage FH. Neurodegenerative disease and adult neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;33:1139–1151. - PubMed
-
- Shirooie S, Nabavi SF, Dehpour AR, Belwal T, Habtemariam S, Argüelles S, et al. Targeting mTORs by omega-3 fatty acids: a possible novel therapeutic strategy for neurodegeneration? Pharmacol Res. 2018;135:37–48. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources