Anti-neoplastic and immunomodulatory potency of co-treatment based on bovine lactoferrin and/or muramyl dipeptide in tumor-bearing mice
- PMID: 32440345
- PMCID: PMC7233322
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa012
Anti-neoplastic and immunomodulatory potency of co-treatment based on bovine lactoferrin and/or muramyl dipeptide in tumor-bearing mice
Abstract
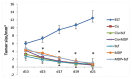
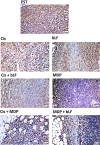
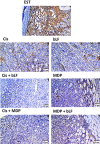
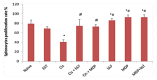
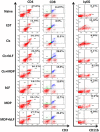
The current study investigates anti-neoplastic and immunomodulatory activities of co-treatment based on bovine lactoferrin (bLF) and/or muramyl dipeptide (MDP) with or without cisplatin (Cis) in tumor-bearing mice. In the present study, bLF (100 mg/kg; orally) and MDP (0.5 mg/kg; subcutaneously) was administered alone or together. MDP or bLF was co-treated with Cis (1 mg/kg; intraperitoneally) in mice-bearing Ehrlich solid carcinoma. Tumor size, tumor mass proliferation, apoptosis using immunohistochemistry, the alteration in spleen cell proliferation, phenotype using flow cytometry and white blood cells total and differential counts were detected. Treatment with Cis or (bLF and MDP) significantly reduced tumor size, upregulated the pro-apoptotic p53 expression and downregulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and proliferative marker PCNA expression compared to non-treated tumor-bearing animals. Moreover, co-treatment of MDP and Cis significantly potentiated the reduction of the tumor size, downregulated the Bcl-2 and PCNA expression and upregulated the p53 expression compared to Cis-treated animals. While bLF and Cis co-treatment positively controlled PCNA and p53 expression compared to tumor-bearing animals, it significantly potentiated the reduction of the tumor size and downregulated the Bcl-2 expression compared to Cis-treated animals. Co-treatment of (bLF and MDP), (bLF and Cis) or (MDP and Cis) increased the spleen cell proliferation and altered the immunological profile of the CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+, CD3+CD4+CD69+, CD3+CD8+CD69+ and CD11b+Ly6G+ cells to achieve better immune response against tumor. In conclusion, co-treatments based on bLF and/or MDP are promising therapies against cancer, through their potency to control proliferation, enhance apoptosis and improve the immune status against tumor cells.
Keywords: apoptosis; cisplatin; immunity; lactoferrin; muramyl dipeptide; tumor.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Physiological and immune response of juvenile rainbow trout to dietary bovine lactoferrin.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Dec;71:359-371. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.10.027. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29050988
-
Inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin on colon carcinoma 26 lung metastasis in mice.Clin Exp Metastasis. 1999 Feb;17(1):35-40. doi: 10.1023/a:1026452110786. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1999. PMID: 10390145
-
Antitumor and immune-modulatory efficacy of dual-treatment based on levamisole and/or taurine in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.113. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29945116
-
LNA aptamer based multi-modal, Fe3O4-saturated lactoferrin (Fe3O4-bLf) nanocarriers for triple positive (EpCAM, CD133, CD44) colon tumor targeting and NIR, MRI and CT imaging.Biomaterials. 2015 Dec;71:84-99. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.055. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26318819
-
Bovine lactoferrin: benefits and mechanism of action against infections.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;84(3):291-6. doi: 10.1139/o06-054. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936799 Review.
Cited by
-
Grape seed extract and L-ascorbic acid exert antineoplastic effects against solid Ehrlich carcinoma in vivo by modulating the tumor microenvironment and Th1/Th2 balance.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 6;16:1635071. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1635071. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40843004 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Drug Sensitisers to Improve Therapeutic Index in Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):928. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070928. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muramyl dipeptide-based analogs as potential anticancer compounds: Strategies to improve selectivity, biocompatibility, and efficiency.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 27;12:970967. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.970967. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36237313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory potencies of cinnamon oil on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma bearing mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 12;12(1):11839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14770-1. Sci Rep. 2022. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 19;15(1):9435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94143-6. PMID: 35821255 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

