Bi-directional Acceleration of Alcohol Use and Opioid Use Disorder
- PMID: 32440365
- PMCID: PMC7241514
Bi-directional Acceleration of Alcohol Use and Opioid Use Disorder
Abstract
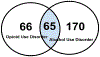
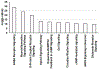
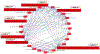
Alcohol is the most widely used addictive substance. Severe alcohol abuse is diagnosed as "alcohol use disorder" (AUD). A common and harmful drinking pattern is binge drinking that elevates a person's blood alcohol concentration to ≥ 0.08%. Such drinking may be an early indicator of AUD. Opioid misuse and dependence have become worldwide crises. Patterned consumption of various opioids can develop into opioid use disorder (OUD). An intertwined epidemic exists between opioid abuse, alcohol addiction, and binge drinking. Currently, studies on the interaction of AUD and OUD are limited and the underlying mechanisms linking these disorders remains unclear. We reviewed studies on AUD and OUD and utilized Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) to identify mechanisms of AUD and OUD interaction and potential gene targets for therapeutic agents. According to IPA Canonical Pathways Analysis, Gamma-aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Receptor Signaling, Neuroinflammation Signaling Pathway, Opioid Signaling Pathway and Dopamine-DARPP32 Feedback in cAMP Signaling are potential contributors to the interaction of AUD and OUD.
Keywords: alcohol abuse; alcohol use disorder; ingenuity pathway analysis; opioid dependence; opioid use disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
8. Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
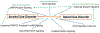
Similar articles
-
Alcohol and Opioid Use, Co-Use, and Chronic Pain in the Context of the Opioid Epidemic: A Critical Review.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018 Mar;42(3):478-488. doi: 10.1111/acer.13594. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018. PMID: 29314075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emergency department presentation of opioid use disorder and alcohol use disorder.J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021 Aug;127:108343. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108343. Epub 2021 Mar 3. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021. PMID: 34134862
-
Nonmedical prescription sedative/tranquilizer use in alcohol and opioid use disorders.Addict Behav. 2019 Jan;88:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Addict Behav. 2019. PMID: 30142484
-
The unique nature of public stigma toward non-medical prescription opioid use and dependence: a national study.Addiction. 2020 Dec;115(12):2317-2326. doi: 10.1111/add.15069. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Addiction. 2020. PMID: 32219910
-
Suicide Risk and Addiction: The Impact of Alcohol and Opioid Use Disorders.Curr Addict Rep. 2021;8(2):194-207. doi: 10.1007/s40429-021-00361-z. Epub 2021 Mar 14. Curr Addict Rep. 2021. PMID: 33747710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Biomarker Identification Using a Network-Based Bioinformatics Approach That Links COVID-19 With Smoking.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2023 Jul 14;17:11779322231186481. doi: 10.1177/11779322231186481. eCollection 2023. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2023. PMID: 37461741 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific Concordance of Striatal Transcriptional Signatures of Opioid Addiction in Human and Rodent Brains.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 24:rs.3.rs-5006061. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5006061/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025 Feb 26;5(3):100476. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2025.100476. PMID: 39399686 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Sex-Specific Concordance of Striatal Transcriptional Signatures of Opioid Addiction in Human and Rodent Brains.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025 Feb 26;5(3):100476. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2025.100476. eCollection 2025 May. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40248277 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid consumption frequency and its associations with potential life problems during opioid agonist treatment in individuals with prescription-type opioid use disorder: exploratory results from the OPTIMA Study.Harm Reduct J. 2025 Feb 8;22(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12954-025-01157-4. Harm Reduct J. 2025. PMID: 39923043 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mukamal KJ, Conigrave KM, Mittleman MA, Camargo CA, Stampfer MJ and Willett WC, et al., Roles of drinking pattern and type of alcohol consumed in coronary heart disease in men, N Engl J Med, 348 (2003), 109–118. - PubMed
-
- Murray RP, Connett JE, Tyas SL, Bond R, Ekuma O and Silversides CK, et al., Alcohol volume, drinking pattern, and cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality: is there a U-shaped function?, Am J Epidemiol,, 155 (2002), 242–248. - PubMed
-
- Rehm J, Greenfield TK and Rogers JD, Average volume of alcohol consumption, patterns of drinking, and all-cause mortality: results from the US National Alcohol Survey, Am J Epidemiol,153 (2001), 64–71. - PubMed
-
- Rehm J, Room R, Graham K, Monteiro M, Gmel G and Sempos CT, The relationship of average volume of alcohol consumption and patterns of drinking to burden of disease: an overview, Addiction, 98 (2003), 1209–1228. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
