Two Non-gadolinium-based, Innovative Approaches to Preoperative Lymphangiography
- PMID: 32440457
- PMCID: PMC7209876
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002805
Two Non-gadolinium-based, Innovative Approaches to Preoperative Lymphangiography
Abstract
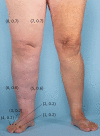
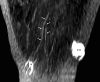
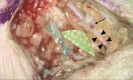
Most magnetic resonance lymphangiography techniques employ intravenous gadolinium-based contrast agents, which carry a US Food and Drug Administration warning about gadolinium retention in the body when used intravenously. Because of this, there may be reluctance to perform intradermal injections of gadolinium-based contrast agents in patients with obstructed lymphatic drainage due to concerns about gadolinium retention in the skin and soft tissues and potential-related toxicity. The aim of this study was to show proof of concept of 2 preoperative lymphangiographic techniques that do not use gadolinium-based contrast agents. One technique used contrast-enhanced ultrasound with intradermal injections of microbubbles (Lumason) in a patient with stage 3, nonpitting left upper extremity edema. Another technique used magnetic resonance imaging with intradermal injections of 0.03 mg/mL or 0.003% ferumoxytol (Feraheme) in a patient with stage 3, nonpitting right lower extremity edema. Both contrast-enhanced ultrasound with microbubbles and magnetic resonance lymphangiogram with ferumoxytol were able to identify candidates for lymphovenous bypass surgery. These candidates were not identified by conventional indocyanine green injections. The authors conclude that (1) low-dose ferumoxytol is a potentially effective non-gadolinium-based contrast alternative to gadolinium-based contrast agent in magnetic resonance lymphangiography and (2) contrast-enhanced ultrasound can identify candidate lymphatic vessels for anastomosis.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Yang JC, Wu SC, Lin WC, et al. Supermicrosurgical lymphaticovenous anastomosis as an alternative treatment option for moderate-to-severe lower limb lymphedema. J Am Coll Surg. 2019 Oct 23. pii: S1072-7515(19)32143-X. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2019.10.007. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Yen YH, Wu SC, et al. Supermicrosurgical lymphaticovenous anastomosis as an alternative treatment option for patients with lymphorrhea. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144:1214–1224. - PubMed
-
- Mitsumori LM, McDonald ES, Wilson GJ, et al. MR lymphangiography: how I do it. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42:1465–1477. - PubMed
-
- Neligan PC, Kung TA, Maki JH. MR lymphangiography in the treatment of lymphedema. J Surg Oncol. 2017;115:18–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
