Hepatocyte TMEM16A Deletion Retards NAFLD Progression by Ameliorating Hepatic Glucose Metabolic Disorder
- PMID: 32440483
- PMCID: PMC7237841
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201903657
Hepatocyte TMEM16A Deletion Retards NAFLD Progression by Ameliorating Hepatic Glucose Metabolic Disorder
Abstract
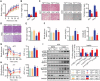
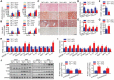
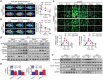
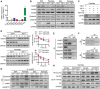
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent form of chronic liver disease, and the mechanisms underpinning its pathogenesis have not been completely established. Transmembrane member 16A (TMEM16A), a component of the Ca2+-activated chloride channel (CaCC), has recently been implicated in metabolic events. Herein, TMEM16A is shown to be responsible for CaCC activation in hepatocytes and is increased in liver tissues of mice and patients with NAFLD. Hepatocyte-specific ablation of TMEM16A in mice ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity, hepatic glucose metabolic disorder, steatosis, insulin resistance, and inflammation. In contrast, hepatocyte-specific TMEM16A transgenic mice exhibit the opposite phenotype. Mechanistically, hepatocyte TMEM16A interacts with vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 (VAMP3) to induce its degradation, suppressing the formation of the VAMP3/syntaxin 4 and VAMP3/synaptosome-associated protein 23 complexes. This leads to the impairment of hepatic glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) translocation and glucose uptake. Notably, VAMP3 overexpression restrains the functions of hepatocyte TMEM16A in blocking GLUT2 translocation and promoting lipid deposition, insulin resistance, and inflammation. In contrast, VAMP3 knockdown reverses the beneficial effects of TMEM16A downregulation. This study demonstrates a role for TMEM16A in NAFLD and suggests that inhibition of hepatic TMEM16A or disruption of TMEM16A/VAMP3 interaction may provide a new potential therapeutic strategy for NAFLD.
Keywords: GLUT2; TMEM16A; VAMP3; glucose metabolic disorder; hepatic steatosis; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte-specific TMEM16A deficiency alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppressing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 26;13(12):1072. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05518-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36572666 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin-2 promotes obesity and progressive fatty liver disease in mice through mechanistically distinct hepatocyte and extra-hepatocyte actions.J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1565-1584. doi: 10.1113/JP277140. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30536914 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor targets hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α and mediates protective effects of vitamin D in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 20;295(12):3891-3905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011487. Epub 2020 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32051143 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin 1 improves hepatic steatosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice and is associated with hepatic fat content in humans.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jul;57:102849. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102849. Epub 2020 Jun 21. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32580141 Free PMC article.
-
Fructose as a key player in the development of fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1166-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1166. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Imbalance of Mitochondrial Homeostasis of Peripheral Blood-Derived Macrophages Mediated by MAFLD May Impair the Walking Ability of Elderly Patients with Osteopenia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 24;2022:5210870. doi: 10.1155/2022/5210870. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35368864 Free PMC article.
-
Anoctamin 1 controls bone resorption by coupling Cl- channel activation with RANKL-RANK signaling transduction.Nat Commun. 2022 May 24;13(1):2899. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30625-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35610255 Free PMC article.
-
Phytic acid-based nanomedicine against mTOR represses lipogenesis and immune response for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis therapy.Life Metab. 2024 Jun 18;3(6):loae026. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/loae026. eCollection 2024 Dec. Life Metab. 2024. PMID: 39873005 Free PMC article.
-
Ponatinib modulates the metabolic profile of obese mice by inhibiting adipose tissue macrophage inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;13:1040999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1040999. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36457708 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract 50 (GBE50) Ameliorates Insulin Resistance, Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice.J Inflamm Res. 2021 May 17;14:1959-1971. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S302934. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34040411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao G. N., Zhang P., Gong J., Zhang X. J., Wang P. X., Yin M., Jiang Z., Shen L. J., Ji Y. X., Tong J., Wang Y., Wei Q. F., Wang Y., Zhu X. Y., Zhang X., Fang J., Xie Q., She Z. G., Wang Z., Huang Z., Li H., Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 742. - PubMed
-
- Fu D., Cui H., Zhang Y., Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2187. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
