Genistein inhibits angiogenesis developed during rheumatoid arthritis through the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/VEGF signalling pathway
- PMID: 32440504
- PMCID: PMC7231959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.07.007
Genistein inhibits angiogenesis developed during rheumatoid arthritis through the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/VEGF signalling pathway
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis plays an important role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which increases the supply of nutrients, cytokines, and inflammatory cells to the synovial membrane. Genistein (GEN), a soy-derived isoflavone, has been validated that can effectively inhibit the angiogenesis of several tumours. We thus carried out a study in vitro to investigate the effect of GEN in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and angiogenesis induced by the inflammatory environment of RA.
Methods: MH7A cells were used to verify whether GEN can inhibit the expression of VEGF in MH7A cells under inflammatory conditions and demonstrate the mechanism. EA.hy926 cells were used to verify whether GEN can inhibit the migration and tube formation of vascular endothelial cells in inflammatory environment.
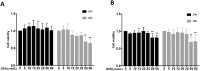
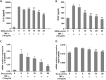
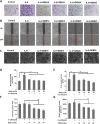
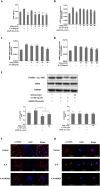
Results: GEN dose-dependently inhibited the expression and secretion of interleukin (IL)-6 and VEGF, as well as the nucleus translocation of Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in MH7A. Furthermore, GEN inhibited IL-6-induced vascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation in vitro.
Conclusion: GEN inhibits IL-6-induced VEGF expression and angiogenesis partially through the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/STAT3 pathway in RA, which has provided a novel insight into the antiangiogenic activity of GEN in RA.
The translational potential of this article: Our study provides scientific guidance for the clinical translational research of GEN in the RA treatment.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Genistein; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-35 Inhibits Angiogenesis through VEGF/Ang2/Tie2 Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):1105-1116. doi: 10.1159/000453165. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27960151
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits VEGF expression induced by IL-6 via Stat3 in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 May 14;17(18):2315-25. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i18.2315. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21633597 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-angiogenic effect of Shikonin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating PI3K/AKT and MAPKs signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:113039. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113039. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32497675
-
The protective effect of natural medicines in rheumatoid arthritis via inhibit angiogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 31;15:1380098. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1380098. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38881875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of vascular endothelial cell-mediated angiogenesis in the imbalance of RA synovial microenvironment and its clinical relevance.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1481089. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1481089. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40255565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Chromatin Landscape of Pathogenic Transcriptional Cell States in Rheumatoid Arthritis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 8:2023.04.07.536026. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.07.536026. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 May 31;15(1):4650. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48620-7. PMID: 37066336 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
[Tujia medicine Toddalia asiatica improves synovial pannus in rats with collagen-induced arthritis through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Aug 20;44(8):1582-1588. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.17. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39276054 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The Effect of STAT3 Signal Pathway Activation on Retinopathy of Prematurity.Front Pediatr. 2021 Nov 10;9:638432. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.638432. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34858895 Free PMC article.
-
[Triptolide inhibits inflammatory response and migration of fibroblast like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis through the circRNA 0003353/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Mar 20;42(3):367-374. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.03.08. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35426800 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The protective activity of genistein against bone and cartilage diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 8;13:1016981. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1016981. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clavel G., Bessis N., Boissier M.-C. Recent data on the role for angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt Bone Spine. 2003;70(5):321–326. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

