Metformin regulates adiponectin signalling in epicardial adipose tissue and reduces atrial fibrillation vulnerability
- PMID: 32441464
- PMCID: PMC7348162
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15407
Metformin regulates adiponectin signalling in epicardial adipose tissue and reduces atrial fibrillation vulnerability
Abstract
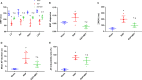
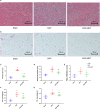
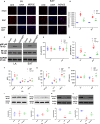
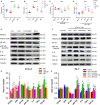
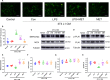
Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) remodelling is closely related to the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation (AF). We investigated whether metformin (MET) prevents AF-dependent EAT remodelling and AF vulnerability in dogs. A canine AF model was developed by 6-week rapid atrial pacing (RAP), and electrophysiological parameters were measured. Effective refractory periods (ERP) were decreased in the left and right atrial appendages as well as in the left atrium (LA) and right atrium (RA). MET attenuated the RAP-induced increase in ERP dispersion, cumulative window of vulnerability, AF inducibility and AF duration. RAP increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) phosphorylation; up-regulated interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) levels in LA and EAT; decreased peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and adiponectin (APN) expression in EAT and was accompanied by atrial fibrosis and adipose infiltration. MET reversed these alterations. In vitro, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure increased IL-6, TNF-α and TGF-β1 expression and decreased PPARγ/APN expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, which were all reversed after MET administration. Indirect coculture of HL-1 cells with LPS-stimulated 3T3-L1 conditioned medium (CM) significantly increased IL-6, TNF-α and TGF-β1 expression and decreased SERCA2a and p-PLN expression, while LPS + MET CM and APN treatment alleviated the inflammatory response and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ handling dysfunction. MET attenuated the RAP-induced increase in AF vulnerability, remodelling of atria and EAT adipokines production profiles. APN may play a key role in the prevention of AF-dependent EAT remodelling and AF vulnerability by MET.
Keywords: adiponectin; atrial fibrillation; epicardial adipose tissue; inflammation; metformin.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relationship that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98:946‐952. - PubMed
-
- Al Chekakie MO, Welles CC, Metoyer R, et al. Pericardial fat is independently associated with human atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:784‐788. - PubMed
-
- Wong CX, Abed HS, Molaee P, et al. Pericardial fat is associated with atrial fibrillation severity and ablation outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1745‐1751. - PubMed
-
- Wong CX, Ganesan AN, Selvanayagam JB. Epicardial fat and atrial fibrillation: current evidence, potential mechanisms, clinical implications, and future directions. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:1294‐1302. - PubMed
-
- Chilukoti RK, Giese A, Malenke W, et al. Atrial fibrillation and rapid acute pacing regulate adipocyte/adipositas‐related gene expression in the atria. Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:604‐613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

