Developmentally Programmed Tankyrase Activity Upregulates β-Catenin and Licenses Progression of Embryonic Genome Activation
- PMID: 32442396
- PMCID: PMC7335218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.04.018
Developmentally Programmed Tankyrase Activity Upregulates β-Catenin and Licenses Progression of Embryonic Genome Activation
Abstract
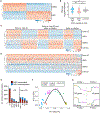
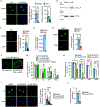
Embryonic genome activation (EGA) is orchestrated by an intrinsic developmental program initiated during oocyte maturation with translation of stored maternal mRNAs. Here, we show that tankyrase, a poly(ADP-ribosyl) polymerase that regulates β-catenin levels, undergoes programmed translation during oocyte maturation and serves an essential role in mouse EGA. Newly translated TNKS triggers proteasomal degradation of axin, reducing targeted destruction of β-catenin and promoting β-catenin-mediated transcription of target genes, including Myc. MYC mediates ribosomal RNA transcription in 2-cell embryos, supporting global protein synthesis. Suppression of tankyrase activity using knockdown or chemical inhibition causes loss of nuclear β-catenin and global reductions in transcription and histone H3 acetylation. Chromatin and transcriptional profiling indicate that development arrests prior to the mid-2-cell stage, mediated in part by reductions in β-catenin and MYC. These findings indicate that post-transcriptional regulation of tankyrase serves as a ligand-independent developmental mechanism for post-translational β-catenin activation and is required to complete EGA.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; WNT signaling pathway; axin; embryonic genome activation; mouse; post-transcriptional regulation; preimplantation embryo; tankyrase; β-catenin.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Adenot PG, Mercier Y, Renard JP, and Thompson EM (1997). Differential H4 acetylation of paternal and maternal chromatin precedes DNA replication and differential transcriptional activity in pronuclei of 1-cell mouse embryos. Development 124, 4615–4625. - PubMed
-
- Angers S, and Moon RT (2009). Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 468–477. - PubMed
-
- Aoki F, Worrad DM, and Schultz RM (1997). Regulation of transcriptional activity during the first and second cell cycles in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Biol 181, 296–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

