Artificial neural networks for magnetic resonance elastography stiffness estimation in inhomogeneous materials
- PMID: 32442867
- PMCID: PMC7583310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101710
Artificial neural networks for magnetic resonance elastography stiffness estimation in inhomogeneous materials
Abstract
Purpose: To test the hypothesis that removing the assumption of material homogeneity will improve the spatial accuracy of stiffness estimates made by Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE).
Methods: An artificial neural network was trained using synthetic wave data computed using a coupled harmonic oscillator model. Material properties were allowed to vary in a piecewise smooth pattern. This neural network inversion (Inhomogeneous Learned Inversion (ILI)) was compared against a previous homogeneous neural network inversion (Homogeneous Learned Inversion (HLI)) and conventional direct inversion (DI) in simulation, phantom, and in-vivo experiments.
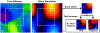
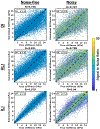
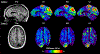
Results: In simulation experiments, ILI was more accurate than HLI and DI in predicting the stiffness of an inclusion in noise-free, low-noise, and high-noise data. In the phantom experiment, ILI delineated inclusions ≤ 2.25 cm in diameter more clearly than HLI and DI, and provided a higher contrast-to-noise ratio for all inclusions. In a series of stiff brain tumors, ILI shows sharper stiffness transitions at the edges of tumors than the other inversions evaluated.
Conclusion: ILI is an artificial neural network based framework for MRE inversion that does not assume homogeneity in material stiffness. Preliminary results suggest that it provides more accurate stiffness estimates and better contrast in small inclusions and at large stiffness gradients than existing algorithms that assume local homogeneity. These results support the need for continued exploration of learning-based approaches to MRE inversion, particularly for applications where high resolution is required.
Keywords: Artificial neural networks; Inversion; Magnetic resonance elastography; Stiffness.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests. A.M., K.P.M., J.D.T., J.H., R.L.E., M.C.M. and Mayo Clinic have a financial conflict of interest related to this research. This research has been reviewed by the Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest Review Board and is being conducted in compliance with Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest policies.
Figures






References
-
- Chollet Francois, 2015. Keras. https://keras.io.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

