Pediatric Endoscopy in the Era of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Position Paper
- PMID: 32443022
- PMCID: PMC7273958
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002750
Pediatric Endoscopy in the Era of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Position Paper
Abstract
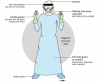
The delivery of endoscopic care is changing rapidly in the era of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). The North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) Endoscopy and Procedures Committee has formulated this statement to offer practical guidance to help standardize endoscopy services for pediatric patients with the aim of minimizing COVID-19 transmission to staff, patients, and caregivers and to conserve personal protective equipment (PPE) during this critical time. Appropriate use of PPE is essential to minimize transmission and preserve supply. Pediatric endoscopic procedures are considered at high risk for COVID-19 transmission. We recommend that all pediatric endoscopic procedures are done in a negative pressure room with all staff using proper airborne, contact, and droplet precautions regardless of patient risk stratification. This includes appropriate use of a filtering face-piece respirator (N95, N99, FFP2/3, or PAPR), double gloves, facial protection (full visor and/or face shield), full body water-resistant disposable gown, shoe covers and a hairnet. In deciding which endoscopic procedures should proceed, it is important to weigh the risks and benefits to optimize healthcare delivery and minimize risk. To inform these decisions, we propose a framework for stratifying procedures as emergent (procedures that need to PROCEEED), urgent (PAUSE, weigh the benefits and risks in deciding whether to proceed) and elective (POSTPONE procedures). This statement was based on emerging evidence and is meant as a guide. It is important that all endoscopy facilities where pediatric procedures are performed follow current recommendations from public health agencies within their jurisdiction regarding infection prevention and control of COVID-19.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pediatric Endoscopy During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Addressing the Implications of Universal Preprocedural Testing for PPE Utilization.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021 Jan 1;72(1):e25-e26. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002962. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33003169 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report. World Health Organization website. Published April 6, 2020. <ext-link xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" ext-link-type="uri" xlink:href="https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...">https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...</ext-link>. Accessed April 21, 2020.
-
- Luthi S. Surgeon General advises hospitals to cancel elective surgeries. Politico website. Published March 14, 2020. <ext-link xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" ext-link-type="uri" xlink:href="https://www.politico.com/news/2020/03/14/surgeon-general-elective-surger...">https://www.politico.com/news/2020/03/14/surgeon-general-elective-surger...</ext-link>. Accessed April 7, 2020.
-
- American College of Surgeons. COVID-19: recommendations for management of elective surgical procedures. American College of Surgeons website. Published March 13, 2020. <ext-link xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" ext-link-type="uri" xlink:href="https://www.facs.org/covid-19/clinical-guidance/elective-surgery">https://www.facs.org/covid-19/clinical-guidance/elective-surgery</ext-link>. Accessed April 7, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical