Identification of crucial genes correlated with esophageal cancer by integrated high-throughput data analysis
- PMID: 32443386
- PMCID: PMC7254712
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020340
Identification of crucial genes correlated with esophageal cancer by integrated high-throughput data analysis
Abstract
Background: Esophageal cancer (ESCA) is one of the most deadly malignancies in the world. Although the management and treatment of patients with ESCA have improved, the overall 5-year survival rate is still very poor.
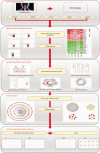
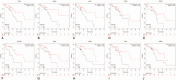
Methods: The study aimed to identify potential key genes associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of ESCA. In the study, integrated bioinformatics methods were used to screen differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between ESCA and normal tissue in the data set of gene expression profiles. The hub gene in DEGs was further analyzed by protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and survival analysis to explore its relationship with the pathogenesis and poor prognosis of ESCA.
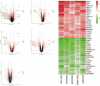
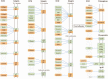
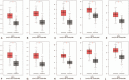
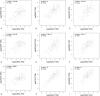
Results: 134 up-regulated genes and 183 down-regulated genes were obtained in ESCA compared with normal tissues. Moreover, the PPI network was established with 176 nodes and 800 interactions. Ten hub genes (AURKA, CDC20, BUB1, TOP2A, ASPM, DLGAP5, TPX2, CENPF, UBE2C, and NEK2) were filtered out based on the degree value. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that a variety of extracellular related items and ECM-receptor interaction pathway were all correlated with the ESCA.
Conclusions: The results of this study would provide some guidance for further study of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers to promote ESCA treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Laversanne M, Brown LM, et al. Predicting the future burden of esophageal cancer by histological subtype: international trends in incidence up to 2030. Am J Gastroenterol 2017;112:1247–55. - PubMed
-
- Toh Y, Oki E, Ohgaki K, et al. Alcohol drinking, cigarette smoking, and the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Oncol 2010;15:135–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

