The Regulation of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier by Myosin Light Chain Kinase/Rho Kinases
- PMID: 32443411
- PMCID: PMC7278945
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21103550
The Regulation of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier by Myosin Light Chain Kinase/Rho Kinases
Abstract
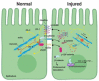
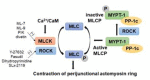
The intestinal epithelial apical junctional complex, which includes tight and adherens junctions, contributes to the intestinal barrier function via their role in regulating paracellular permeability. Myosin light chain II (MLC-2), has been shown to be a critical regulatory protein in altering paracellular permeability during gastrointestinal disorders. Previous studies have demonstrated that phosphorylation of MLC-2 is a biochemical marker for perijunctional actomyosin ring contraction, which increases paracellular permeability by regulating the apical junctional complex. The phosphorylation of MLC-2 is dominantly regulated by myosin light chain kinase- (MLCK-) and Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase- (ROCK-) mediated pathways. In this review, we aim to summarize the current state of knowledge regarding the role of MLCK- and ROCK-mediated pathways in the regulation of the intestinal barrier during normal homeostasis and digestive diseases. Additionally, we will also suggest potential therapeutic targeting of MLCK- and ROCK-associated pathways in gastrointestinal disorders that compromise the intestinal barrier.
Keywords: adherens junction; apical junction complex; myosin light chain kinase; rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Das P., Goswami P., Das T.K., Nag T., Sreenivas V., Ahuja V., Panda S.K., Gupta S.D., Makharia G.K. Comparative tight junction protein expressions in colonic Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and tuberculosis: A new perspective. Virchows Arch. 2012;460:261–270. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1195-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

