Anti-Hypertensive Activity of Novel Peptides Identified from Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Surimi
- PMID: 32443419
- PMCID: PMC7278688
- DOI: 10.3390/foods9050647
Anti-Hypertensive Activity of Novel Peptides Identified from Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Surimi
Abstract
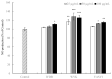
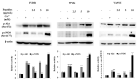
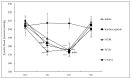
There is a growing interest in the health benefits of functional foods. A benefit that has been long sought is the control of hypertension through dietary approaches. Hypertension has been implicated as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and is therefore of clinical significance. Here, we aim to demonstrate the antihypertensive activity of novel peptides derived from surimi, a functional food ingredient made from refined fish myofibrillar proteins. Three peptides, Ile-Val-Asp-Arg (IVDR), Trp-Tyr-Lys (WYK), and Val-Ala-Ser-Val-Ile (VASVI), were isolated from surimi made from the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Our results show that IVDR, WYK, and VASVI exhibited high Angiotensin I-converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibition activity. These peptides are also shown to increase phosphorylation of protein kinase B (Akt) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and significantly promote nitric oxide (NO) production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Oral administration of the peptides decreased blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), thereby confirming that the peptides derived from surimi perform antihypertensive activity via the Akt/eNOS pathway. These results indicate that surimi made from P. olivaceus contains novel antihypertensive peptides that could be used to enhance the health benefits of food ingredients.
Keywords: Paralichthys olivaceus; antihypertensive; peptide; surimi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Endogenous Cathepsin L in Muscle Protein Degradation in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Surimi Gel.Molecules. 2021 Mar 28;26(7):1901. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071901. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33800606 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant activity of olive flounder (Paralichthya olivaceus) surimi digest in in vitro and in vivo.J Food Sci Technol. 2022 May;59(5):2071-2079. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-05221-2. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35531393 Free PMC article.
-
Eight antihypertensive peptides from the protein hydrolysate of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): Isolation, identification, and activity evaluation on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).Food Res Int. 2019 Jul;121:197-204. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.035. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31108740
-
Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins.Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2015;6:235-62. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-022814-015520. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25884281 Review.
-
[Peptides with antihypertensive activity from milk and egg proteins].Nutr Hosp. 2008 Jul-Aug;23(4):313-8. Nutr Hosp. 2008. PMID: 18604316 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Food-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides in Regulating the Key Factors of the Renin-Angiotensin System.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 29;17(1):97. doi: 10.3390/nu17010097. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent findings on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of novel food-derived antihypertensive peptides.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Jan 25;4:100078. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100078. eCollection 2022 Jul 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35415696 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive Effect of Milk Fermented by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K79 on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Jan;44(1):178-188. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2023.e70. Epub 2024 Jan 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 38229853 Free PMC article.
-
Selenized Chickpea Sprouts Hydrolysates as a Potential Anti-Aging Ingredient.Molecules. 2023 Apr 12;28(8):3402. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083402. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110634 Free PMC article.
-
Abalone Viscera Fermented with Aspergillus oryzae 001 Prevents Pressure Elevation by Inhibiting Angiotensin Converting Enzyme.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 14;15(4):947. doi: 10.3390/nu15040947. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Causes of Death 2008: Data Sources and Methods. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
-
- Wu S., Feng X., Lan X., Xu Y., Liao D. Purification and identification of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods. 2015;13:295–299. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.12.051. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

