Clustering and Kernel Density Estimation for Assessment of Measurable Residual Disease by Flow Cytometry
- PMID: 32443428
- PMCID: PMC7277972
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10050317
Clustering and Kernel Density Estimation for Assessment of Measurable Residual Disease by Flow Cytometry
Abstract
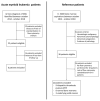
Standardization, data mining techniques, and comparison to normality are changing the landscape of multiparameter flow cytometry in clinical hematology. On the basis of these principles, a strategy was developed for measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment. Herein, suspicious cell clusters are first identified at diagnosis using a clustering algorithm. Subsequently, automated multidimensional spaces, named "Clouds", are created around these clusters on the basis of density calculations. This step identifies the immunophenotypic pattern of the suspicious cell clusters. Thereafter, using reference samples, the "Abnormality Ratio" (AR) of each Cloud is calculated, and major malignant Clouds are retained, known as "Leukemic Clouds" (L-Clouds). In follow-up samples, MRD is identified when more cells fall into a patient's L-Cloud compared to reference samples (AR concept). This workflow was applied on simulated data and real-life leukemia flow cytometry data. On simulated data, strong patient-dependent positive correlation (R2 = 1) was observed between the AR and spiked-in leukemia cells. On real patient data, AR kinetics was in line with the clinical evolution for five out of six patients. In conclusion, we present a convenient flow cytometry data analysis approach for the follow-up of hematological malignancies. Further evaluation and validation on more patient samples and different flow cytometry panels is required before implementation in clinical practice.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia (AML); clustering; flow cytometry; kernel density estimation; multiparametric data analysis; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Da Costa E.S., Pedreira C.E., Barrena S., Lécrevisse Q., Flores-Montero J., Quijano S., Almeida J., Macias M.D.C.G., Böttcher S., Van Dongen J.J., et al. Automated pattern-guided principal component analysis vs expert-based immunophenotypic classification of B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders: A step forward in the standardization of clinical immunophenotyping. Leukemia. 2010;24:1927–1933. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalina T., Flores-Montero J., Van Der Velden V.H.J., Martín-Ayuso M., Böttcher S., Ritgen M., Almeida J., Lhermitte L., Asnafi V., Mendonça A., et al. EuroFlow standardization of flow cytometer instrument settings and immunophenotyping protocols. Leukemia. 2012;26:1986–2010. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lacombe F., Dupont B., Lechevalier N., Vial J.-P., Pigneux A., Bene M.C. New Concepts of Flow Cytometry Analysis in Oncohematology: Application to Diagnosis and Follow up (Minimal Residual Disease) in AML, ALL and MDS. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl. 1)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

