A Single Shot Pre-fusion-Stabilized Bovine RSV F Vaccine is Safe and Effective in Newborn Calves with Maternally Derived Antibodies
- PMID: 32443437
- PMCID: PMC7349975
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8020231
A Single Shot Pre-fusion-Stabilized Bovine RSV F Vaccine is Safe and Effective in Newborn Calves with Maternally Derived Antibodies
Abstract
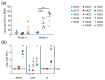
Achieving safe and protective vaccination against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants and in calves has proven a challenging task. The design of recombinant antigens with a conformation close to their native form in virus particles is a major breakthrough. We compared two subunit vaccines, the bovine RSV (BRSV) pre-fusion F (preF) alone or with nanorings formed by the RSV nucleoprotein (preF+N). PreF and N proteins are potent antigenic targets for neutralizing antibodies and T cell responses, respectively. To tackle the challenges of neonatal immunization, three groups of six one-month-old calves with maternally derived serum antibodies (MDA) to BRSV received a single intramuscular injection of PreF, preF+N with MontanideTM ISA61 VG (ISA61) as adjuvant or only ISA61 (control). One month later, all calves were challenged with BRSV and monitored for virus replication in the upper respiratory tract and for clinical signs of disease over one week, and then post-mortem examinations of their lungs were performed. Both preF and preF+N vaccines afforded safe, clinical, and virological protection against BRSV, with little difference between the two subunit vaccines. Analysis of immune parameters pointed to neutralizing antibodies and antibodies to preF as being significant correlates of protection. Thus, a single shot vaccination with preF appears sufficient to reduce the burden of BRSV disease in calves with MDA.
Keywords: bovine; neonate; pre-fusion conformation; respiratory syncytial virus; subunit vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Nair H., Nokes D.J., Gessner B.D., Dherani M., Madhi S.A., Singleton R.J., O’Brien K.L., Roca A., Wright P.F., Bruce N., et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:1545–1555. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60206-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi T., McAllister D.A., O’Brien K.L., Simoes E.A.F., Madhi S.A., Gessner B.D., Polack F.P., Balsells E., Acacio S., Aguayo C., et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. 2017;390:946–958. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

