Human Spinal Motor Neurons Are Particularly Vulnerable to Cerebrospinal Fluid of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients
- PMID: 32443559
- PMCID: PMC7278966
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21103564
Human Spinal Motor Neurons Are Particularly Vulnerable to Cerebrospinal Fluid of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
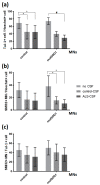
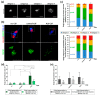
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most common and devastating motor neuron (MN) disease. Its pathophysiological cascade is still enigmatic. More than 90% of ALS patients suffer from sporadic ALS, which makes it specifically demanding to generate appropriate model systems. One interesting aspect considering the seeding, spreading and further disease development of ALS is the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). We therefore asked whether CSF from sporadic ALS patients is capable of causing disease typical changes in human patient-derived spinal MN cultures and thus could represent a novel model system for sporadic ALS. By using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived MNs from healthy controls and monogenetic forms of ALS we could demonstrate a harmful effect of ALS-CSF on healthy donor-derived human MNs. Golgi fragmentation-a typical finding in lower organism models and human postmortem tissue-was induced solely by addition of ALS-CSF, but not control-CSF. No other neurodegenerative hallmarks-including pathological protein aggregation-were found, underpinning Golgi fragmentation as early event in the neurodegenerative cascade. Of note, these changes occurred predominantly in MNs, the cell type primarily affected in ALS. We thus present a novel way to model early features of sporadic ALS.
Keywords: ALS; Golgi fragmentation; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; cerebrospinal fluid; fused in sarcoma; superoxide dismutase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gomez-Pinedo U., Galan L., Yanez M., Matias-Guiu J., Valencia C., Guerrero-Sola A., Lopez-Sosa F., Brin J.R., Benito-Martin M.S., Leon-Espinosa G., et al. Histological changes in the rat brain and spinal cord following prolonged intracerebroventricular infusion of cerebrospinal fluid from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients are similar to those caused by the disease. Neurologia. 2018;33:211–223. doi: 10.1016/j.nrleng.2016.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Pinedo U., Yanez M., Matias-Guiu J., Galan L., Guerrero-Sola A., Benito-Martin M.S., Vela A., Arranz-Tagarro J.A., Garcia A.G. Cellular changes in motor neuron cell culture produced by cytotoxic cerebrospinal fluid from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurologia. 2014;29:346–352. doi: 10.1016/j.nrl.2013.08.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

