A Bibliometric Review of Publications on Oxidative Stress and Chemobrain: 1990-2019
- PMID: 32443630
- PMCID: PMC7278845
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9050439
A Bibliometric Review of Publications on Oxidative Stress and Chemobrain: 1990-2019
Abstract
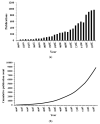
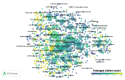
Oxidative stress is considered one of the possible mechanisms behind chemobrain or the cognitive dysfunction persistent after chemotherapy treatment. Breast cancer patients have reported chemobrain symptoms since the 1990s. In this present bibliometric review, we employed the VOSviewer tool to describe the existing landscape on literature concerning oxidative stress, breast cancer chemotherapies, and chemobrain. As of 2019, 8799 papers were listed in the Web of Science database, with more than 900 papers published each year. As expected, terms relating to oxidative stress, mitochondria, breast cancer, and antioxidants have occurred very often in the literature throughout the years. In recent years, there has been an increase in the occurrence of terms related to nanomedicine. Only within the last decade do the keywords 'brain', 'blood-brain barrier', and 'central nervous system' appear, reflecting an increased interest in chemobrain. China has become the most prolific producer of oxidative stress and chemotherapy related papers in the last decade followed by the USA and India. In conclusion, the subject of oxidative stress as a mechanism behind chemotherapies' toxicities is an active area of research.
Keywords: antioxidants; chemobrain; chemotherapy; cognitive dysfunction; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

