Early-Life Programming and Reprogramming of Adult Kidney Disease and Hypertension: The Interplay between Maternal Nutrition and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 32443635
- PMCID: PMC7278949
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21103572
Early-Life Programming and Reprogramming of Adult Kidney Disease and Hypertension: The Interplay between Maternal Nutrition and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
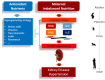
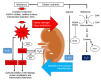
Kidney disease and hypertension both have attained the status of a global pandemic. Altered renal programming resulting in kidney disease and hypertension can begin in utero. Maternal suboptimal nutrition and oxidative stress have important implications in renal programming, while specific antioxidant nutrient supplementations may serve as reprogramming strategies to prevent kidney disease and hypertension of developmental origins. This review aims to summarize current knowledge on the interplay of maternal nutrition and oxidative stress in response to early-life insults and its impact on developmental programming of kidney disease and hypertension, covering two aspects. Firstly, we present the evidence from animal models supporting the implication of oxidative stress on adult kidney disease and hypertension programmed by suboptimal maternal nutrition. In the second part, we document data on specific antioxidant nutrients as reprogramming strategies to protect adult offspring against kidney disease and hypertension from developmental origins. Research into the prevention of kidney disease and hypertension that begin early in life will have profound implications for future health.
Keywords: antioxidant; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD); hydrogen sulfide; hypertension; kidney disease; nitric oxide; nutrition; offspring; oxidative stress; pregnancy; reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

