Effect of HIIT with Tabata Protocol on Serum Irisin, Physical Performance, and Body Composition in Men
- PMID: 32443802
- PMCID: PMC7277607
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17103589
Effect of HIIT with Tabata Protocol on Serum Irisin, Physical Performance, and Body Composition in Men
Abstract
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is frequently utilized as a method to reduce body mass. Its intensity of work results in a number of beneficial adaptive changes in a relatively short period of time. Irisin is a myokine and adipokine secreted to the blood during exercise and it takes part in the regulation of energy metabolism. It is a vital issue from the prophylaxis point of view as well as treatment through exercise of different diseases (e.g., obesity, type-2 diabetes). The aim of this study was to evaluate changes in irisin concentration, body composition, and aerobic and anaerobic performance in men after HIIT. Eight weeks of HIIT following the Tabata protocol was applied in the training group (HT) (n = 15), while a sedentary group (SED) (n = 10) did not participate in fitness activities within the same time period. Changes of irisin, body composition, and aerobic and anaerobic performance were evaluated after graded exercise test (GXT) and Wingate anaerobic test (WAnT) before and after eight weeks of training. Training resulted in an increased of blood irisin concentration (by 29.7%) p < 0.05), VO2max increase (PRE: 44.86 ± 5.74 mL·kg-1·min-1; POST: 50.16 ± 5.80 mL kg-1·min-1; p < 0.05), reduction in percent body fat (PRE: 14.44 ± 3.33%; POST: 13.61 ± 3.16%; p < 0.05), and increase of WAnT parameters (p < 0.05) in the HT group. No changes were observed in the SED group. HIIT resulted in beneficial effects in the increase in blood irisin concentration, physical performance, and reduced fat content. The HIIT may indicate an acceleration of base metabolism. This effect can be utilized in the prevention or treatment of obesity.
Keywords: HIIT; basal metabolism; fat reduction; fitness; health; irisin; lean body mass; power output.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
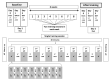
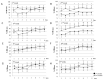
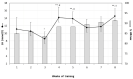
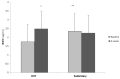
References
-
- Bartlett J.D., Close G.L., MacLaren D.P., Gregson W., Drust B., Morton J.P. High-intensity interval running is perceived to be more enjoyable than moderate-intensity continuous exercise: Implications for exercise adherence. J. Sports Sci. 2011;29:547–553. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2010.545427. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

