Effects of the Positive Allosteric Modulator of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5, VU-29, on Maintenance Association between Environmental Cues and Rewarding Properties of Ethanol in Rats
- PMID: 32443872
- PMCID: PMC7277181
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10050793
Effects of the Positive Allosteric Modulator of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5, VU-29, on Maintenance Association between Environmental Cues and Rewarding Properties of Ethanol in Rats
Abstract
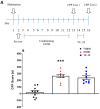
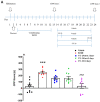
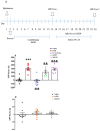
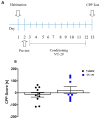
: Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 (mGlu5) receptors are implicated in various forms of synaptic plasticity, including drugs of abuse. In drug-addicted individuals, associative memories can drive relapse to drug use. The present study investigated the potential of the mGlu5 receptor positive allosteric modulator (PAM), VU-29 (30 mg/kg, i.p.), to inhibit the maintenance of a learned association between ethanol and environmental context by using conditioned place preference (CPP) in rats. The ethanol-CPP was established by the administration of ethanol (1.0 g/kg, i.p. × 10 days) using an unbiased procedure. Following ethanol conditioning, VU-29 was administered at various post-conditioning times (ethanol free state at the home cage) to ascertain if there was a temporal window during which VU-29 would be effective. Our experiments indicated that VU-29 did not affect the expression of ethanol-induced CPP when it was given over two post-conditioning days. However, the expression of ethanol-CPP was inhibited by 10-day home cage administration of VU-29, but not by first 2-day or last 2-day injection of VU-29 during the 10-day period. These findings reveal that VU-29 can inhibit the maintenance of ethanol-induced CPP, and that treatment duration contributes to this effect of VU-29. Furthermore, VU-29 effect was reversed by pretreatment with either MTEP (the mGlu5 receptor antagonist), or MK-801 (the N-methyl-D-aspartate-NMDA receptor antagonist). Thus, the inhibitory effect of VU-29 is dependent on the functional interaction between mGlu5 and NMDA receptors. Because a reduction in ethanol-associated cues can reduce relapse, mGlu5 receptor PAM would be useful for therapy of alcoholism. Future research is required to confirm the current findings.
Keywords: VU-29; conditioned place preference; ethanol; mGlu5 receptor; memory; positive allosteric modulator; reward.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Niaura R.S., Rohsenow D.J., Binkoff J.A., Monti P.M., Pedraza M., Abrams D.B. Relevance of cue reactivity to understanding alcohol and smoking relapse. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1988;97:133–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

