Patatin-Related Phospholipase pPLAIIIγ Involved in Osmotic and Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 32443904
- PMCID: PMC7284883
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9050650
Patatin-Related Phospholipase pPLAIIIγ Involved in Osmotic and Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis
Abstract
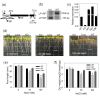
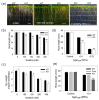
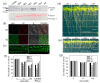
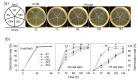
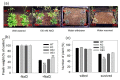
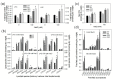
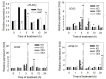
Patatinrelated phospholipases (pPLAs) are acylhydrolyzing enzymes implicated in various processes, including lipid metabolism, signal transduction, plant growth and stress responses, but the function for many specific pPLAs in plants remains unknown. Here we determine the effect of patatinrelated phospholipase A pPLAIIIγ on Arabidopsis response to abiotic stress. Knockout of pPLAIIIγ rendered plants more sensitive whereas overexpression of pPLAIIIγ enhanced plant tolerance to NaCl and drought in seed germination and seedling growth. The pPLAIIIγknockout and overexpressing seedlings displayed a lower and higher level of lysolipids and free fatty acids than that of wildtype plants in response to NaCl stress, respectively. These results indicate that pPLAIIIγ acts a positive regulator of salt and osmatic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; abiotic stress; free fatty acid; lysophospholipids; patatinrelated phospholipase A; signaling mediators.
Conflict of interest statement
The corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

