Implementing volunteer-navigation for older persons with advanced chronic illness (Nav-CARE): a knowledge to action study
- PMID: 32443979
- PMCID: PMC7245025
- DOI: 10.1186/s12904-020-00578-1
Implementing volunteer-navigation for older persons with advanced chronic illness (Nav-CARE): a knowledge to action study
Abstract
Background: Nav-CARE is a volunteer-led intervention designed to build upon strategic directions in palliative care: a palliative approach to care, a public health/compassionate community approach to care, and enhancing the capacity of volunteerism. Nav-CARE uses specially trained volunteers to provide lay navigation for older persons and family living at home with advanced chronic illness. The goal of this study was to better understand the implementation factors that influenced the utilization of Nav-CARE in eight diverse Canadian contexts.
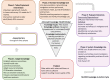
Methods: This was a Knowledge to Action study using the planned action cycle for Nav-CARE developed through previous studies. Participants were eight community-based hospice societies located in diverse geographic contexts and with diverse capacities. Implementation data was collected at baseline, midpoint, and endpoint using qualitative individual and group interviews. Field notes of all interactions with study sites were also used as part of the data set. Data was analyzed using qualitative descriptive techniques. The study received ethical approval from three university behavioural review boards. All participants provided written consent.
Results: At baseline, stakeholders perceived Nav-CARE to be a good fit with the strategic directions of their organization by providing early palliative support, by facilitating outreach into the community and by changing the public perception of palliative care. The contextual factors that determined the ease with which Nav-CARE was implemented included the volunteer coordinator champion, organizational capacity and connection, the ability to successfully recruit older persons, and the adequacy of volunteer preparation and mentorship.
Conclusions: This study highlighted the importance of community-based champions for the success of volunteer-led initiatives and the critical need for support and mentorship for both volunteers and those who lead them. Further, although the underutilization of hospice has been widely recognized, it is vital to recognize the limitations of their capacity. New initiatives such as Nav-CARE, which are designed to enhance their contributions to palliative care, need to be accompanied by adequate resources. Finally, this study illustrated the need to think carefully about the language and role of hospice societies as palliative care moves toward a public health approach to care.
Keywords: (3–10) volunteers; Compassionate community; Hospice; Knowledge translation; Navigation; Palliative; Palliative approach; Public-health.
Conflict of interest statement
BP, WD, GW, EK, PB, EA, BH declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mason B, Nanton V, Epiphaniou E, Murray SA, Donaldson A, Shipman C, et al. ‘My body is falling apart’. Understanding the experiences of patients with advanced multimorbidity to improve care: serial interviews with patients and carers. Brit Med J. 2016;6:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Walke L, Gallo W, Tinetti M, Fried T. The burden of symptoms among community-dwelling olderpersons with advanced chronic disease. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:2321–2324. - PubMed
-
- National Seniors Council . Report on the social isolation of seniors. 2014.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

