Cytomegalovirus inhibition of extrinsic apoptosis determines fitness and resistance to cytotoxic CD8 T cells
- PMID: 32444487
- PMCID: PMC7293702
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1914667117
Cytomegalovirus inhibition of extrinsic apoptosis determines fitness and resistance to cytotoxic CD8 T cells
Erratum in
-
Correction for Chaudhry et al., Cytomegalovirus inhibition of extrinsic apoptosis determines fitness and resistance to cytotoxic CD8 T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 11;117(32):19606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014825117. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32747538 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
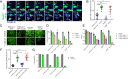
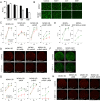
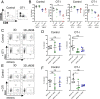
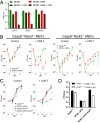
Viral immune evasion is currently understood to focus on deflecting CD8 T cell recognition of infected cells by disrupting antigen presentation pathways. We evaluated viral interference with the ultimate step in cytotoxic T cell function, the death of infected cells. The viral inhibitor of caspase-8 activation (vICA) conserved in human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and murine CMV (MCMV) prevents the activation of caspase-8 and proapoptotic signaling. We demonstrate the key role of vICA from either virus, in deflecting antigen-specific CD8 T cell-killing of infected cells. vICA-deficient mutants, lacking either UL36 or M36, exhibit greater susceptibility to CD8 T cell control than mutants lacking the set of immunoevasins known to disrupt antigen presentation via MHC class I. This difference is evident during infection in the natural mouse host infected with MCMV, in settings where virus-specific CD8 T cells are adoptively transferred. Finally, we identify the molecular mechanism through which vICA acts, demonstrating the central contribution of caspase-8 signaling at a point of convergence of death receptor-induced apoptosis and perforin/granzyme-dependent cytotoxicity.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; apoptosis; apoptosis inhibition; cytomegalovirus; immune evasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF Signaling Dictates Myeloid and Non-Myeloid Cell Crosstalk to Execute MCMV-Induced Extrinsic Apoptosis.Viruses. 2020 Oct 28;12(11):1221. doi: 10.3390/v12111221. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33126536 Free PMC article.
-
UL36 Rescues Apoptosis Inhibition and In vivo Replication of a Chimeric MCMV Lacking the M36 Gene.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 14;7:312. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00312. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28770171 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus pp65- and immediate early 1 antigen-specific HLA class I-restricted cytotoxic T cell responses induced by cross-presentation of viral antigens.J Immunol. 2001 May 1;166(9):5695-703. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.9.5695. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11313411
-
In vivo impact of cytomegalovirus evasion of CD8 T-cell immunity: facts and thoughts based on murine models.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):161-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.022. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20933556 Review.
-
Caspase-8-dependent control of NK- and T cell responses during cytomegalovirus infection.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Aug;208(3-4):555-571. doi: 10.1007/s00430-019-00616-7. Epub 2019 May 16. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31098689 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis Disorder, a Key Pathogenesis of HCMV-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global cis-regulatory landscape of double-stranded DNA viruses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 20:2025.07.20.665756. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.20.665756. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791439 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Programmed Necrosis in Host Defense.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023;442:1-40. doi: 10.1007/82_2023_264. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37563336
-
Targeted T cell receptor gene editing provides predictable T cell product function for immunotherapy.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Aug 17;2(8):100374. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100374. eCollection 2021 Aug 17. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34467251 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of CMV infection on the viability of cardiac cells.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Apr 3;9(1):111. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01408-y. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37012234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGeoch D. J., Cook S., Dolan A., Jamieson F. E., Telford E. A., Molecular phylogeny and evolutionary timescale for the family of mammalian herpesviruses. J. Mol. Biol. 247, 443–458 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Lin A., Xu H., Yan W., Modulation of HLA expression in human cytomegalovirus immune evasion. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 4, 91–98 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Quinnan G. V. Jr. et al. ., Cytotoxic t cells in cytomegalovirus infection: HLA-restricted T-lymphocyte and non-T-lymphocyte cytotoxic responses correlate with recovery from cytomegalovirus infection in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 307, 7–13 (1982). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

