The FBW7-MCL-1 axis is key in M1 and M2 macrophage-related colon cancer cell progression: validating the immunotherapeutic value of targeting PI3Kγ
- PMID: 32444799
- PMCID: PMC7272616
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-020-0436-7
The FBW7-MCL-1 axis is key in M1 and M2 macrophage-related colon cancer cell progression: validating the immunotherapeutic value of targeting PI3Kγ
Abstract
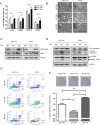
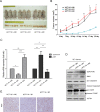
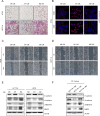
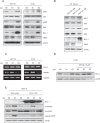
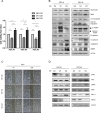
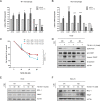
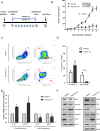
Colorectal cancer is a devastating disease with a low 5-year survival rate. Recently, many researchers have studied the mechanisms of tumor progression related to the tumor microenvironment. Here, we addressed the prognostic value of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) using a total of 232 CRC patient tissue samples and investigated the mechanisms underlying TAM-related colon cancer progression with respect to PI3Kγ regulation using in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo approaches. Patients with M2/M1 < 3 had significantly improved progression-free survival and overall survival compared with patients with M2/M1 > 3. M1 and M2 macrophages elicited opposite effects on colon cancer progression via the FBW7-MCL-1 axis. Blocking macrophage PI3Kγ had cytotoxic effects on colon cancer cells and inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition features by regulating the FBW7-MCL-1 axis. The results of this study suggest that macrophage PI3Kγ may be a promising target for immunotherapy in colon cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE. The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:618–631. - PubMed
-
- Pollard JW. Tumour-educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Ostuni R, Kratochvill F, Murray PJ, Natoli G. Macrophages and cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Trends Immunol. 2015;36:229–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

