Isatuximab plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients with renal impairment: ICARIA-MM subgroup analysis
- PMID: 32444867
- PMCID: PMC7862055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-0868-z
Isatuximab plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients with renal impairment: ICARIA-MM subgroup analysis
Abstract
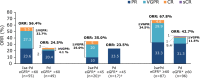
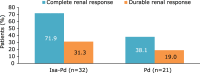
The randomized, phase 3 ICARIA-MM study investigated isatuximab (Isa) with pomalidomide and dexamethasone (Pd) versus Pd in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma and ≥2 prior lines. This prespecified subgroup analysis examined efficacy in patients with renal impairment (RI; estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m²). Isa 10 mg/kg was given intravenously once weekly in cycle 1, and every 2 weeks in subsequent 28-day cycles. Patients received standard doses of Pd. Median progression-free survival (PFS) for patients with RI was 9.5 months with Isa-Pd (n = 55) and 3.7 months with Pd (n = 49; hazard ratio [HR] 0.50; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.30-0.85). Without RI, median PFS was 12.7 months with Isa-Pd (n = 87) and 7.9 months with Pd (n = 96; HR 0.58; 95% CI, 0.38-0.88). The overall response rate (ORR) with and without RI was higher with Isa-Pd (56 and 68%) than Pd (25 and 43%). Complete renal response rates were 71.9% (23/32) with Isa-Pd and 38.1% (8/21) with Pd; these lasted ≥60 days in 31.3% (10/32) and 19.0% (4/21) of patients, respectively. Isa pharmacokinetics were comparable between the subgroups, suggesting no need for dose adjustment in patients with RI. In summary, the addition of Isa to Pd improved PFS, ORR and renal response rates.
Conflict of interest statement
MAD: Consultancy: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen; Honoraria: Amgen, Celgene. SJH: Consultancy: Amgen, Sanofi, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen-Cilag, Karyopharm, Takeda, Haemalogix; Research funding: Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis; Patent: Novartis (panobinostat). HMP: Consultancy: Amgen, Sanofi, Celgene, Novartis; Research funding: Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis. EMO: Research support: Amgen, Array BioPharma, Celgene, IDP-Pharma, Mundipharma; Honoraria: Janssen, Amgen, MSD, Asofarma, BMS, Takeda; Consultancy: Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, Sanofi, Secura Bio, Oncopeptides, Mundipharma, Takeda. SA, FC, LM, DS: Employment: Sanofi. HvdV: Employment: Sanofi; Stock Ownership: Sanofi. KY: Consultancy: Autolus; Honoraria: Amgen, Sanofi, Celgene, Takeda, Roche; Research funding: Sanofi, Celgene, Amgen.
Figures


References
-
- San-Miguel JF, Hungria VT, Yoon SS, Beksac M, Dimopoulos MA, Elghandour A, et al. Panobinostat plus bortezomib and dexamethasone versus placebo plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1195–206. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70440-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

