Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 via Close Contact and Respiratory Droplets Among Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Mice
- PMID: 32444876
- PMCID: PMC7313959
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa281
Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 via Close Contact and Respiratory Droplets Among Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Mice
Abstract
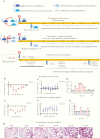
We simulated 3 transmission modes, including close-contact, respiratory droplets and aerosol routes, in the laboratory. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can be highly transmitted among naive human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) mice via close contact because 7 of 13 naive hACE2 mice were SARS-CoV-2 antibody seropositive 14 days after being introduced into the same cage with 3 infected-hACE2 mice. For respiratory droplets, SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from 3 of 10 naive hACE2 mice showed seropositivity 14 days after introduction into the same cage with 3 infected-hACE2 mice, separated by grids. In addition, hACE2 mice cannot be experimentally infected via aerosol inoculation until continued up to 25 minutes with high viral concentrations.
Keywords: SARS-COV-2; aerosol; close contact; hACE2 transgenic mice; respiratory droplets; transmission routes.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Bao L, Deng W, Huang B, et al. . The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice. Nature doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2312-y. - PubMed
-
- Yang XH, Deng W, Tong Z, et al. . Mice transgenic for human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 provide a model for SARS coronavirus infection. Comp Med 2007; 57:450–9. - PubMed
-
- Xu L, Bao L, Deng W, et al. . Novel avian-origin human influenza A(H7N9) can be transmitted between ferrets via respiratory droplets. J Infect Dis 2014; 209:551–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

