Impact of the COVID-19 Outbreak on the Management of Patients with Cancer
- PMID: 32445083
- PMCID: PMC7243433
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-020-00721-1
Impact of the COVID-19 Outbreak on the Management of Patients with Cancer
Abstract
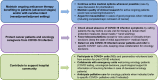
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) outbreak is having a profound impact on the management of patients with cancer. In this review, we comprehensively investigate the various aspects of cancer care during the pandemic, taking advantage of data generated in Asia and Europe at the frontline of the COVID-19 pandemic spread. Cancer wards have been subjected to several modifications to protect patients and healthcare professionals from COVID-19 infection, while attempting to maintain cancer diagnosis, therapy, and research. In this setting, the management of COVID-19 infected patients with cancer is particularly challenging. We also discuss the direct and potential remote impacts of the global pandemic on the mortality of patients with cancer. As such, the indirect impact of the pandemic on the global economy and the potential consequences in terms of cancer mortality are discussed. As the infection is spreading worldwide, we are obtaining more knowledge on the COVID-19 pandemic consequences that are currently impacting and may continue to further challenge cancer care in several countries.
Conflict of interest statement
Eric Raymond has provided consulting for SCOR and Genoscience Pharma. Catherine Thieblemont declares Honoraria, Consulting, and an advisory role with Amgen, Celgene, Jazz Pharma, Kyte, Novartis, Servier, and Roche as well as institutional research funding from Roche, Celgene, and Hospira. Severine Alran and Sandrine Faivre declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

