Sodium status and kidney involvement during COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 32445872
- PMCID: PMC7240271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198034
Sodium status and kidney involvement during COVID-19 infection
Abstract
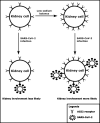
The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (ACE2) is expressed in epithelial cells of many tissues including the kidney, and has been identified to interact with human pathogenic coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Although diffuse alveolar damage and acute respiratory failure are the main features of COVID-19 infection, two recent studies demonstrate that kidney impairment in hospitalized COVID-19 patients is common, and that kidney involvement is associated with high risk of in-hospital death. Interestingly, studies in rats have demonstrated that high dietary sodium intake results in down-regulation of the ACE2 expression in kidney tissue. We hypothesize that low sodium status makes kidney involvement during the course of COVID-19 infection more likely due to upregulation of membrane bound ACE2 in the kidneys. We propose that sodium intake and status should be monitored carefully during severe COVID-19 infections, and that low sodium intake be corrected early in its course, despite a potential conflict regarding common dietary recommendations to restrict dietary sodium intake in patients with hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease.
Keywords: ACE2 receptor; COVID-19; Kidney; SARS-CoV-2; Sodium.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous