Coronavirus disease 2019 in children: Characteristics, antimicrobial treatment, and outcomes
- PMID: 32446167
- PMCID: PMC7204737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104425
Coronavirus disease 2019 in children: Characteristics, antimicrobial treatment, and outcomes
Abstract
Background: At present, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has spread in many countries. We conducted this study to help pediatricians understand the conditions of COVID-19 in children.
Methods: We retrospectively summarized the characteristics, treatment and outcomes of pediatric cases in Wuhan Children's Hospital which was the only designated hospital for children with COVID-19 in Hubei Province. A Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to evaluate factors associated with clinical outcomes.
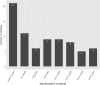
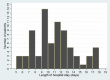
Results: As of February 29, 75 children had been discharged, of which only one was has severe pneumonia and one was critical cases. Children younger than 2 years were more susceptible to COVID-19. All patients have received interferon-α nebulization, and eight cases including the severe and critical cases were co-administrated ribavirin. Five patients with mild pneumonia were given arbidol. Twenty-three patients were given traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The average length of stay (LOS) and the time of SARS-CoV-2 clearance were 10.57 and 6.39 days, respectively. None of the factors was associated with LOS or time of SARS-CoV-2 clearance.
Conclusions: The severity of COVID-19 in pediatric cases were milder than adults. The efficacy of the antiviral therapy in children with COVID-19 remains to be evaluated.
Keywords: Characteristics; Coronavirus disease 2019; Outcomes; Pediatric; Treatment.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest All authors certify no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pediatric Branch of Hubei Medical Association, Pediatric Branch of Wuhan Medical Association, Pediatric Medical Quality Control Center of Hubei [Recommendation for the diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus infection in children in Hubei (Trial version 1)] Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020;22(2):96–99. (in Chinese) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Medical Association Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Journal of Pediatrics Editorial Board [Recommendations for the diagnosis, prevention and control of the 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children (first interim edition)] Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020;58(0):E004. (in Chinese) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous