Long non-coding RNA VIM Antisense RNA 1 (VIM-AS1) sponges microRNA-29 to participate in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 32447557
- PMCID: PMC7413870
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-020-01536-2
Long non-coding RNA VIM Antisense RNA 1 (VIM-AS1) sponges microRNA-29 to participate in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Aims: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) VIM Antisense RNA 1 (VIM-AS1) has been reported to be correlated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptibility, while the roles of this lncRNA in T2D and its complications remain unclear. This study aimed to explore the role of VIM-AS1 in diabetic retinopathy (DR).
Methods: Gene expression levels in both human specimens and in vitro cultivated cells were determined by qPCR and western blot. Overexpression experiments were performed to analyze gene interactions. Cell apoptosis after transfections was detected by cell apoptosis assay.
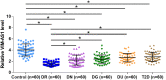
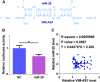
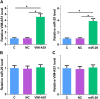
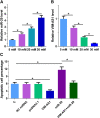
Results: We found that VIM-AS1 was significantly downregulated in T2D patients in comparison with that in healthy controls. Specifically, the expression levels of VIM-AS1 were lowest among T2D patients complicated with DR. Bioinformatics analysis showed that VIM-AS1 can interact with microRNA 29 (miR-29), which is a critical player in high glucose-induced apoptosis of human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPEs). Dual-luciferase assay also revealed the direct interaction between them. High glucose treatment led to upregulated miR-29 and downregulated VIM-AS1. However, overexpression of VIM-AS1 and miR-29 did not affect the expression of each other. Cell apoptosis analysis showed that overexpression of VIM-AS1 reduced the enhancing effects of miR-29 overexpression on RPEs cell proliferation.
Conclusions: Therefore, VIM-AS1 may sponge miR-29 to participate in DR.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Diabetic retinopathy; Retinal pigment epithelial cell; T2D; VIM-AS1; miR-29.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of long noncoding RNA VIM-AS1 and CTBP1-AS2 expression in type 2 diabetes.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):9315-9323. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28206. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30506719
-
LncRNA AK077216 is downregulated in diabetic retinopathy and inhibited the apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelial cells by downregulating miR-383.Endocr J. 2019 Nov 28;66(11):1011-1016. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0080. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Endocr J. 2019. PMID: 31391356
-
Involvement of long non-coding RNA ZNF503 antisense RNA 1 in diabetic retinopathy and its possible underlying mechanism.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14057-14065. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2062988. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35734878 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 1;240:117019. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117019. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31678554 Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Type 2 Diabetes Retinopathy: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10502. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910502. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638838 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
12-HETE activates Müller glial cells: The potential role of GPR31 and miR-29.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2024 Apr;171:106805. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2023.106805. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2024. PMID: 38141777 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Diabetic Retinopathy: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):9829-9860. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04863-z. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40164888 Review.
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives of non-coding RNA-modulated apoptotic signaling in diabetic retinopathy.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jul 6;40(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09896-z. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38970639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs Are Promising Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Retinopathy: An Updated Review (2017-2022).Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 28;12(12):1774. doi: 10.3390/biom12121774. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNAs LY86-AS1 and VIM-AS1 Distinguish Plasma Cell Leukemia Patients from Multiple Myeloma Patients.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 8;9(11):1637. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111637. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829867 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

