[Clinical and coagulation characteristics in 7 patients with critical COVID-2019 pneumonia and acro-ischemia]
- PMID: 32447934
- PMCID: PMC7364914
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.008
[Clinical and coagulation characteristics in 7 patients with critical COVID-2019 pneumonia and acro-ischemia]
Abstract
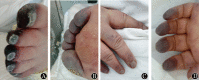
Objective: To investigate the clinical and coagulation characteristics in patients with critical Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and acro-ischemia. Methods: The retrospective study included 7 critical COVID-19 patients with acro-ischemia in an intensive care unit (ICU) in Wuhan, from Feb 4 to Feb 15, 2020. The clinical and laboratory data before and during the ICU stay were analyzed. Results: The median age of 7 patients was 59 years and 4 of them were men. Three patients were associated with underlying comorbidities. Fever, cough, dyspnea and diarrhea were common clinical symptoms. All patients had acro-ischemia presentations including finger/toe cyanosis, skin bulla and dry gangrene. D-dimer, fibrinogen and fibrinogen degradation product (FDP) were significantly elevated in most patients. Prothrombin time was prolonged in 4 patients. D-dimer and FDP levels progressively elevated consistent with COVID-2019 exacerbation. Four patients were diagnosed with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) . Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) was administrated in 6 patients, which reduced D-dimer and FDP rather than improved clinical symptoms. Five patients died finally and the median time from acro-ischemia to death was 12 days. Conclusions: Coagulation parameters should be monitored closely in critical COVID-2019 patients. The timing and protocol of anticoagulation therapy are still under investigation based on more clinical data.
目的: 总结合并肢端缺血的新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)患者的临床和凝血功能特征。 方法: 回顾性分析2020年2月5日至2020年2月15日北京协和医院国家医疗队在武汉收治的7例危重型COVID-19患者临床及实验室资料。 结果: 7例患者中男性4例,女性3例,中位年龄59(49~71)岁,3例合并基础病。发热7例,干咳6例,呼吸困难4例,腹泻4例。所有患者均存在不同程度的肢端缺血,表现为肢端青斑或青紫、血疱、干性坏疽等。7例患者入住重症监护室时均存在D-二聚体显著升高、血小板计数正常,6例纤维蛋白原及纤维蛋白降解产物(FDP)升高,4例凝血酶原时间延长。随着病情进展,D-二聚体及FDP进行性升高,4例患者符合2017年中国弥散性血管内凝血诊断标准。6例患者接受低分子肝素治疗,治疗后D-二聚体及FDP下降,但临床症状无明显好转。中位随访26 d,5例患者死亡,从出现肢端缺血症状至死亡的中位时间为12(7~16)d。 结论: 部分危重型COVID-19患者存在明显高凝倾向,应关注此类患者凝血功能,及时识别高凝期并予抗凝治疗,肢端缺血提示预后不良。抗凝治疗能否改善预后仍需更多临床数据。.
Keywords: Anticoagulation therapy; COVID-2019; Critical; Hypercoagulation status.
Figures
Comment in
-
Anticardiolipin antibodies and COVID-19-A case report from America.J Med Virol. 2021 Jan;93(1):76-77. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26135. Epub 2020 Jun 16. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32497287 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cutaneous manifestations in a series of 417 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: epidemiological and clinical correlates of chilblain like lesions.Pathog Glob Health. 2021 Oct-Dec;115(7-8):483-486. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2021.1901040. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Pathog Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33729097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 国家卫生健康委员会. 新型冠状病毒肺炎诊疗方案(试行第七版)[Z] 2020年3月, 国卫办公函[2020]184号.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical