Subcellular location prediction of apoptosis proteins using two novel feature extraction methods based on evolutionary information and LDA
- PMID: 32448129
- PMCID: PMC7245797
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-020-3539-1
Subcellular location prediction of apoptosis proteins using two novel feature extraction methods based on evolutionary information and LDA
Abstract
Background: Apoptosis, also called programmed cell death, refers to the spontaneous and orderly death of cells controlled by genes in order to maintain a stable internal environment. Identifying the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins is very helpful in understanding the mechanism of apoptosis and designing drugs. Therefore, the subcellular localization of apoptosis proteins has attracted increased attention in computational biology. Effective feature extraction methods play a critical role in predicting the subcellular location of proteins.
Results: In this paper, we proposed two novel feature extraction methods based on evolutionary information. One of the features obtained the evolutionary information via the transition matrix of the consensus sequence (CTM). And the other utilized the evolutionary information from PSSM based on absolute entropy correlation analysis (AECA-PSSM). After fusing the two kinds of features, linear discriminant analysis (LDA) was used to reduce the dimension of the proposed features. Finally, the support vector machine (SVM) was adopted to predict the protein subcellular locations. The proposed CTM-AECA-PSSM-LDA subcellular location prediction method was evaluated using the CL317 dataset and ZW225 dataset. By jackknife test, the overall accuracy was 99.7% (CL317) and 95.6% (ZW225) respectively.
Conclusions: The experimental results show that the proposed method which is hopefully to be a complementary tool for the existing methods of subcellular localization, can effectively extract more abundant features of protein sequence and is feasible in predicting the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins.
Keywords: Absolute entropy correlation analysis; Consensus sequence; Linear discriminant analysis; Position-specific scoring matrix; Subcellular location.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

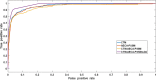


References
-
- Linn F, Charlotte S, Marie S, Martin H, Kalle J, Mikaela W, Annica A, Mathias U, Emma L. Mapping the subcellular protein distribution in three human cell lines. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(8):3766–77. - PubMed
-
- Guo-Sheng H, Zu-Guo Y, Vo A. Predicting the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on recurrence quantification analysis and the hilbert-huang transform. Chinese Physics B. 2011;20(10):100504.
-
- Zhang Z-H, Wang Z-H, Zhang Z-R, Wang Y-X. A novel method for apoptosis protein subcellular localization prediction combining encoding based on grouped weight and support vector machine. FEBS Lett. 2006;580(26):6169–74. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-L, Li Q-Z. Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins. J Theor Biol. 2007;245(4):775–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

