Profiles of Staphyloccocus aureus isolated from goat persistent mastitis before and after treatment with enrofloxacin
- PMID: 32448145
- PMCID: PMC7245832
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-01793-9
Profiles of Staphyloccocus aureus isolated from goat persistent mastitis before and after treatment with enrofloxacin
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is one of the main causative agents of mastitis in small ruminants. Antimicrobial use is the major treatment, but there are many flaws linked to resistance, tolerance or persistence. This study aimed to verify changes in resistance, virulence and clonal profiles of S. aureus isolated from persistent mastitis goat milk before and after enrofloxacin treatment.
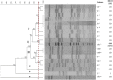
Results: MIC increased to at least one antimicrobial in S. aureus isolates after enrofloxacin treatment compared to before. The most detected resistance genes before and after treatment were tetK, tetM, and blaZ, with more resistance genes detected after enrofloxacin treatment (p < 0.05). Occasional variations in efflux system gene detection were observed before and after treatment. Nine virulence genes (hla, fnbA, fnbB, eta, etb, sea, sec, seh, and sej) were detected at both times, and between these, the hla and eta genes were detected more in isolates after treatment. All isolates of S. aureus belonged to the same sequence type (ST) 133, except for two S. aureus isolates prior to enrofloxacin treatment which were classified as ST5 and the other as a new one, ST4966. Isolates of S. aureus 4, 8, and 100 from before and after treatment had identical pulse types, while others obtained from other animals before and after treatment were classified into distinct pulse types.
Conclusion: There were occasional changes in the studied profiles of S. aureus isolated before and after treatment of animals with enrofloxacin, which may have contributed to the permanence of bacteria in the mammary gland, even when using traditional treatment, resulting in persistent mastitis.
Keywords: Caprine mastitis; Persistence; Small ruminants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multilocus sequence analysis reveals genetic diversity in Staphylococcus aureus isolate of goat with mastitis persistent after treatment with enrofloxacin.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 26;11(1):17252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96764-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34446803 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristic profiles of molecular types, antibiotic resistance, antibiotic resistance genes, and virulence genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from caprine mastitis in China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 18;15:1533844. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1533844. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40041149 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Ruminants with Mastitis in Northern Greece Dairy Herds: Genetic Relatedness and Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;13(3):176. doi: 10.3390/toxins13030176. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668901 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020 Sep;22:792-802. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.06.010. Epub 2020 Jun 27. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020. PMID: 32603906 Review.
-
Emerging insights of Staphylococcus spp. in human mastitis.Microb Pathog. 2025 Aug;205:107685. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107685. Epub 2025 May 9. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40349998 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes of Bacterial Pathogens from Bovine and Caprine Mastitis in Northern Lebanon.Microorganisms. 2021 May 27;9(6):1148. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061148. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34071800 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus sequence analysis reveals genetic diversity in Staphylococcus aureus isolate of goat with mastitis persistent after treatment with enrofloxacin.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 26;11(1):17252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96764-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34446803 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance, Enterotoxin and mec Gene Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Beef-Based Protein Sources from KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 14;10(6):1211. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061211. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744729 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of listing and categorisation of animal diseases within the framework of the Animal Health Law (Regulation (EU) No 2016/429): antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in cattle and horses.EFSA J. 2022 May 10;20(5):e07312. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7312. eCollection 2022 May. EFSA J. 2022. PMID: 35582361 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Degraded Limonoid Analogs as New Antibacterial Scaffolds against Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 6;9(8):488. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080488. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32781770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergonier D, de Crémoux R, Rupp R, Lagriffoul G, Berthelot X. Mastitis of dairy small ruminants. Vet Res. 2003;34:689–716. - PubMed
-
- Attili AR, Preziuso S, Ngwa VN, Cantalamessa A, Moriconi M, Cuteri V. Clinical evaluation of the use of enrofloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus clinical mastitis in sheep. Small Rumin Res. 2016;136:72–77.
-
- Brauner A, Fridman O, Gefen O, Balaban NQ. Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14:320–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

