Identification of novel biomarkers for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy using iTRAQ
- PMID: 32448169
- PMCID: PMC7245890
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-020-00822-7
Identification of novel biomarkers for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy using iTRAQ
Abstract
Background: A prompt diagnosis of HIE remains a challenge clinically. This study aimed to identify potential biomarkers of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) via a novel proteomic approach, the isobaric tags for absolute and relative quantification (iTRAQ) method.
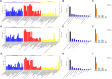
Methods: Blood samples were collected from neonates with mild (n = 4), moderate (n = 4), or severe (n = 4) HIE who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of Children's Hospital of Soochow University between Oct 2015 and Oct 2017. iTRAQ was performed in HIE patients and healthy controls (n = 4). Bioinformatics analyses including Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis were performed to evaluate the potential features and capabilities of the identified differentially expressed proteins.
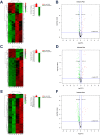
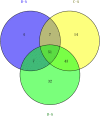
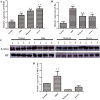
Results: A total of 51 commonly differentially expressed proteins were identified among the comparisons between mild, moderate, and severe HIE as well as healthy controls. Haptoglobin (HP) and S100A8 were most significantly up-regulated in patients with HIE and further validated via real-time PCR and western blotting. The differentially expressed proteins represented multiple biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions and were markedly enriched in complement and coagulation cascades.
Conclusions: HP and S100A8 may serve as a potential biomarker for neonatal HIE and reflects the severity of HIE. The complement and coagulation cascades play crucial roles in the development of neonatal HIE.
Keywords: Haptoglobin; Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; Isobaric tags for absolute and relative quantification; Neonate; S100A8.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative proteomic analysis for non-invasive early prediction of hypoxic-ischemic injury in asphyxiated neonates.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2024 Mar;18(2):e2200054. doi: 10.1002/prca.202200054. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2024. PMID: 37787895
-
Study of Cord Blood Erythropoietin, Leptin and Adiponectin Levels in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020;20(2):213-220. doi: 10.2174/1871530319666190725110619. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 31345155
-
Serum cytokine profiling in neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2021;14(2):177-182. doi: 10.3233/NPM-200431. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2021. PMID: 33074195
-
Severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and heart rate variability in neonates: a systematic review.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jul 19;19(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1603-7. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31324176 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy-related biomarkers in serum and cerebrospinal fluid.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Oct 23;450:282-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.08.021. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26320853 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying Early Diagnostic Biomarkers Associated with Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 18;11(5):897. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050897. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070031 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics in Neonatal/Pediatric Medicine-A Literature Review.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 18;14(7):767. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070767. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39064021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Roles of the "Omics" in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in Neonates.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;9(10):498. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9100498. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis identifying proteins relevant for treatment success following experimental neonatal inflammation-sensitized hypoxia-ischemia.Pediatr Res. 2025 May 13. doi: 10.1038/s41390-025-04097-8. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Res. 2025. PMID: 40360774
-
Peptidomic Analysis of Neonate Umbilical Cord Blood for the Identification of Endogenous Peptides Involved in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy.Front Pediatr. 2021 Aug 25;9:718704. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.718704. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34513766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shao XM, Ye H, Qiu XS. Practical newborn[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: People′s Medical Publishing House; 2011. p. 395.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81671532/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81471488, 81771625/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81871193/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZDXKA2016013/Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline
- BE2015644/Jiangsu Province Key Research and Development of Special Funds in China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

