Transgenerational inheritance of fetal alcohol exposure adverse effects on immune gene interferon-ϒ
- PMID: 32448218
- PMCID: PMC7245772
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-020-00859-9
Transgenerational inheritance of fetal alcohol exposure adverse effects on immune gene interferon-ϒ
Abstract
Background: Alcohol exposures in utero have been shown to alter immune system functions in the offspring which persists into adulthood. However, it is not apparent why the in utero alcohol effect on the immune system persists into adulthood of fetal alcohol-exposed offspring. The objective of this study was to determine the long-term effects of fetal alcohol exposure on the production of interferon-ϒ (IFN-ϒ), a cytokine known to regulate both innate and adaptive immunity.
Methods: Isogenic Fisher 344 rats were bred to produce pregnant dams, which were fed with a liquid diet containing 6.7% alcohol between gestation days 7 and 21 and pair-fed with an isocaloric liquid diet or fed ad libitum with rat chow; their male and female offspring were used for the study. F1-F3 generation rats were used when they were 2 to 3 months old. Fetal alcohol exposure effects on the Ifn-ɣ gene was determined by measuring the gene promoter methylation and mRNA and protein expression in the spleen. Additionally, transgenerational studies were conducted to evaluate the germline-transmitted effects of fetal alcohol exposure on the Ifn-ɣ gene.
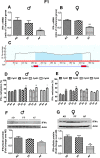
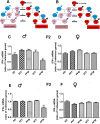
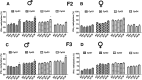
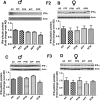
Results: Fetal alcohol exposure reduced the expression of Ifn-ɣ mRNA and IFN-ϒ protein while it increased the proximal promoter methylation of the Ifn-ɣ gene in both male and female offspring during the adult period. Transgenerational studies revealed that the reduced levels of Ifn-ɣ expression and increased levels of its promoter methylation persisted only in F2 and F3 generation males derived from the male germ line.
Conclusion: Overall, these findings provide the evidence that fetal alcohol exposures produce an epigenetic mark on the Ifn-ɣ gene that passes through multiple generations via the male germ line. These data provide the first evidence that the male germ line transmits fetal alcohol exposure's adverse effects on the immune system.
Keywords: Epigenetic; Fetal alcohol; Interferon-ϒ; Transgenerational transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Male germline transmits fetal alcohol adverse effect on hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin gene across generations.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep 1;72(5):378-88. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.04.006. Epub 2012 May 22. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22622000 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational inheritance of fetal alcohol effects on proopiomelanocortin gene expression and methylation, cortisol response to stress, and anxiety-like behaviors in offspring for three generations in rats: Evidence for male germline transmission.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 10;17(2):e0263340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263340. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35143549 Free PMC article.
-
Pesticide methoxychlor promotes the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of adult-onset disease through the female germline.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 24;9(7):e102091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102091. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25057798 Free PMC article.
-
Male germline transmits fetal alcohol epigenetic marks for multiple generations: a review.Addict Biol. 2016 Jan;21(1):23-34. doi: 10.1111/adb.12186. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Addict Biol. 2016. PMID: 25581210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
Cited by
-
Single-nucleus resolution mapping of the adult C. elegans and its application to elucidate inter- and trans-generational response to alcohol.Cell Rep. 2023 Jun 27;42(6):112535. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112535. Epub 2023 May 23. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37227821 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational Effects of Prenatal Ethanol Exposure in Prepubescent Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 21;10:812429. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.812429. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35386207 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal preconception donepezil exposure enhances learning in offspring.Behav Brain Funct. 2024 Sep 28;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12993-024-00252-z. Behav Brain Funct. 2024. PMID: 39342229 Free PMC article.
-
Do Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance and Immune System Development Share Common Epigenetic Processes?J Dev Biol. 2021 May 12;9(2):20. doi: 10.3390/jdb9020020. J Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34065783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Determining Region Y Controls the Effects of Fetal Alcohol Exposure on Proopiomelanocortin Gene Expression.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 16;15:608102. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.608102. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33796006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gauthier TW, Drews-Botsch C, Falek A, Coles C, Brown LA. Maternal alcohol abuse and neonatal infection. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29(6):1035–1043. - PubMed
-
- Kesmodel U, Olsen SF, Secher NJ. Does alcohol increase the risk of preterm delivery? Epidemiology. 2000;11(5):512–518. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary CM, Nassar N, Kurinczuk JJ, Bower C. The effect of maternal alcohol consumption on fetal growth and preterm birth. BJOG. 2009;116(3):390–400. - PubMed
-
- Sokol RJ, Janisse JJ, Louis JM, Bailey BN, Ager J, Jacobson SW, Jacobson JL. Extreme prematurity: an alcohol-related birth effect. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31(6):1031–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

